8 Essential Principles for How to Lift Heavier Weights are progressive overload, proper form, adequate rest, compound movements, consistent training, proper nutrition, mental preparation, and recovery optimization.
Learning how to lift heavier weights requires systematic progression, proper technique, and understanding of strength training principles that maximize your lifting capacity safely and effectively. Understanding how to lift heavier weights helps you break through plateaus while building impressive strength and muscle mass through proven methods and consistent application.
Table of Contents
8 Essential Principles for How to Lift Heavier Weights.
Mastering how to lift heavier weights requires understanding the fundamental principles that drive strength development and progressive overload. This comprehensive breakdown reveals the key factors that determine your ability to increase lifting capacity safely and effectively.
| Principle | Impact Level | Time to Results | Key Focus |
| 1. Progressive Overload | High | 2-4 weeks | Gradual weight increase |
| 2. Proper Form | High | Immediate | Safe technique |
| 3. Adequate Rest | High | 1-2 weeks | Recovery between sets |
| 4. Compound Movements | High | 4-6 weeks | Multi-muscle exercises |
| 5. Consistent Training | Medium | 6-8 weeks | Regular schedule |
| 6. Proper Nutrition | Medium | 2-6 weeks | Fuel for strength |
| 7. Mental Preparation | Medium | 1-3 weeks | Confidence building |
| 8. Recovery Optimization | High | 2-4 weeks | Sleep and rest |
Learn how many calories do you burn doing 100 sit ups and the breakdown of how many calories are burned in sit ups.
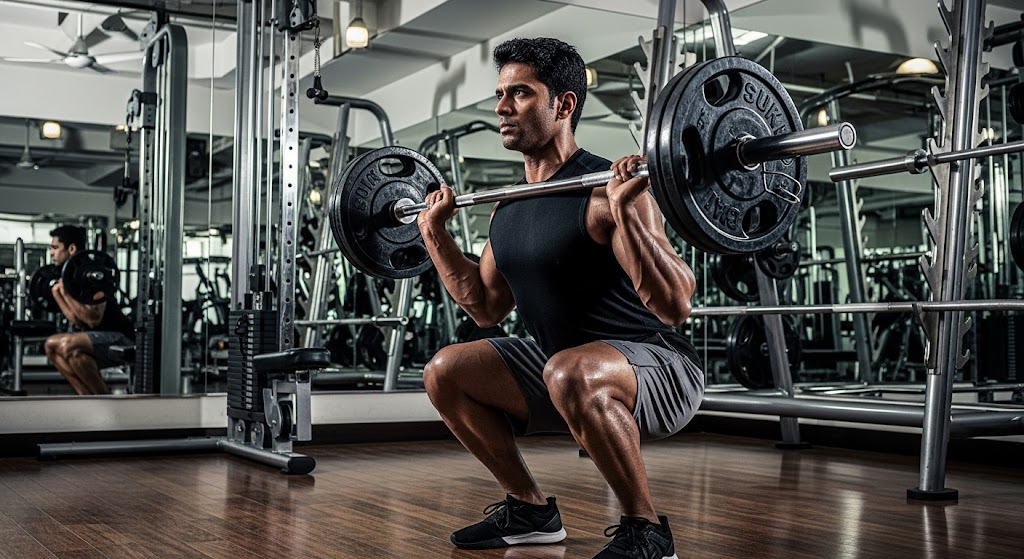

1. Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the fundamental principle for how to lift heavier weights, requiring you to gradually increase weight, repetitions, or training volume over time. This systematic progression forces your muscles to adapt and grow stronger while preventing plateaus.
2. Proper Form
Maintaining proper form is crucial when learning how to lift heavier weights safely and effectively. Good technique ensures optimal muscle engagement, prevents injury, and allows for consistent progression without compromising safety.
3. Adequate Rest
Proper rest between sets is essential for how to lift heavier weights with maximum effort. Adequate recovery allows your muscles to replenish energy stores and maintain strength throughout your workout session.
4. Compound Movements
Focusing on compound exercises is key for how to lift heavier weights efficiently. These multi-joint movements engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, allowing you to handle more weight and build functional strength.
5. Consistent Training
Regular training consistency is vital for how to lift heavier weights over time. Frequent practice reinforces movement patterns while providing consistent stimulus for strength adaptation and improvement.
6. Proper Nutrition
Adequate nutrition supports your ability to lift heavier weights by providing energy for workouts and nutrients for muscle recovery. Proper fueling enhances performance and accelerates strength gains.
7. Mental Preparation
Mental readiness significantly impacts how to lift heavier weights successfully. Confidence, focus, and positive mindset contribute to breaking through mental barriers that often limit physical performance.
8. Recovery Optimization
Quality sleep and recovery directly influence how to lift heavier weights in subsequent sessions. Proper rest allows muscle repair, nervous system recovery, and strength adaptations to occur.
Find out are burpees good for belly fat. Start with calisthenics at home no equipment.
Low Reps Heavy Weight vs High Reps Light Weight
Understanding the physiological differences between heavy and light weight training helps optimize program design for specific goals. Each approach triggers different adaptations through distinct mechanisms, making neither inherently superior but rather complementary for comprehensive development. Smart programming often incorporates both approaches strategically throughout training cycles for maximum benefit.
Training Method Comparison
| Factor | Low Reps Heavy Weight (1-6 reps) | High Reps Light Weight (12-20+ reps) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Adaptation | Maximal strength, neural efficiency | Muscular endurance, metabolic capacity |
| Load Range | 80-95%+ of 1RM | 50-70% of 1RM |
| Rest Periods | 3-5+ minutes between sets | 30-90 seconds between sets |
| Muscle Growth | Moderate (strength-focused) | Moderate to high (volume-dependent) |
| Neural Adaptations | Very high (motor unit recruitment) | Low to moderate |
| Metabolic Stress | Low | Very high |
| Time Under Tension | Low per set | High per set |
| Injury Risk | Higher (heavy loads) | Lower (lighter loads) |
| Technical Demands | Very high | Moderate |
| Beginner Suitability | Not recommended | More suitable |
| Fatigue Recovery | 72-96+ hours | 24-48 hours |
| Joint Stress | High | Moderate |
| Cardiovascular Benefit | Minimal | Moderate to high |

How Long Does It Take to Go Up in Weight Lifting?
Weightlifting progression timelines vary significantly based on training experience, genetics, consistency, and starting strength levels. Beginners may see strength increases weekly for several months, while advanced lifters might take months to add meaningful weight to their lifts.
Individual factors including age, training history, recovery capacity, and adherence to programming dramatically influence progression rates. Realistic expectations prevent disappointment while maintaining motivation for long-term strength development. Most lifters experience rapid initial gains followed by progressively slower improvements requiring greater patience and more sophisticated programming approaches.
Starting with proper warm up exercises for beginners before attempting heavier loads prepares your body and reduces injury risk.
Powerlifting Strength Program
Powerlifting programs focus specifically on maximizing performance in squat, bench press, and deadlift through specialized training methods. These programs emphasize heavy loading, competition-specific movements, and progressive overload. Proper powerlifting programming requires solid technique foundation and should only be attempted by lifters with adequate training experience to handle demanding workloads safely.
Sample 12-Week Powerlifting Program Structure
| Week | Intensity Focus | Volume | Squat Focus | Bench Focus | Deadlift Focus | Accessory Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | Technique/Base | High | 70-80% 5×5 | 70-80% 5×5 | 70-80% 5×3 | General strength |
| 4-6 | Strength Build | Medium-High | 80-85% 4×3 | 80-85% 4×3 | 80-85% 4×2 | Weak point focus |
| 7-9 | Intensity Build | Medium | 85-90% 3×2 | 85-90% 3×2 | 85-90% 3×1 | Competition prep |
| 10-11 | Peak/Test | Low | 90-100% singles | 90-100% singles | 90-100% singles | Minimal |
| 12 | Competition/Max | Very Low | Opener/2nd/3rd | Opener/2nd/3rd | Opener/2nd/3rd | None |
Training Frequency and Structure
- Squat: 2-3 times per week with varying intensities
- Bench Press: 2-3 times per week including pause practice
- Deadlift: 1-2 times per week (high CNS demand)
- Accessory Work: 2-4 exercises targeting weak points
- Rest Days: Minimum 1 full rest day per week
Progressive Overload Methods for Lifting Heavier
Learning how to lift heavier weights requires understanding different progressive overload methods that systematically increase training demands. Each method provides unique benefits for strength development and helps prevent training plateaus.
| Method | Description | Best For | Progression Rate |
| Weight Increase | Add more weight to the bar | Strength building | 2.5-5 kg per week |
| Volume Increase | More sets or repetitions | Muscle building | 1-2 reps per week |
| Frequency Increase | More training sessions | Work capacity | 1 session per month |
| Density Increase | Same work, less time | Conditioning | Reduce rest by 30 seconds |
| Range Increase | Greater range of motion | Flexibility strength | Gradual progression |
| Tempo Manipulation | Slower or faster reps | Specific adaptations | Weekly changes |
| Exercise Progression | Harder exercise variations | Skill development | Monthly progressions |
| Load Distribution | Better weight distribution | Stability | As needed |
How to Get Stronger to Lift Heavier Weights?
Understanding how to get stronger to lift heavier weights requires addressing multiple factors that contribute to strength development. These strategies work together to maximize your lifting potential through comprehensive strength building approaches.
- Strength Training Specificity Focus your training on exercises that directly relate to the lifts you want to improve. Specificity in movement patterns and muscle groups enhances your ability to lift heavier weights in target exercises.
- Neural Adaptations Early strength gains come from improved nervous system efficiency rather than muscle growth. Learning how to get stronger to lift heavier weights involves training your nervous system to recruit muscle fibers more effectively.
- Muscle Hypertrophy Building muscle mass provides the foundation for long-term strength development. Larger muscles have greater potential for force production, supporting your goal to lift heavier weights.
- Technical Proficiency Perfecting lifting technique allows you to express your strength more efficiently. Better form means more of your strength goes into moving the weight rather than fighting poor positioning, which is essential for learning how to lift heavier weights consistently.
Many people wonder does calisthenics build muscle effectively? Combining bodyweight training with weight lifting creates comprehensive strength development.
How to Lift More Weight?
Lifting more weight requires systematic progression, proper technique, and patience rather than rushing through increases that compromise form or safety. Sustainable strength gains come through consistent training, adequate recovery, and gradual overload. Smart programming and attention to weak points create lasting strength improvements while minimizing injury risk that could derail progress entirely.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Strength Progression
- Master Perfect Technique First: Develop flawless form with lighter weights before attempting heavier loads, as technique breaks down under excessive weight and increases injury risk
- Use Progressive Overload Systematically: Add 2.5-5 pounds per week for upper body exercises and 5-10 pounds for lower body movements, allowing adequate time for adaptation
- Focus on Compound Movements: Prioritize squats, deadlifts, bench press, and overhead press as they engage multiple muscle groups and allow for greater loading potential
- Address Weak Points Specifically: Identify limiting factors in your lifts and target them with accessory exercises to eliminate bottlenecks in strength development
- Prioritize Recovery and Sleep: Strength gains occur during rest periods, so ensure 7-9 hours of quality sleep and 48-72 hours between training same muscle groups
- Maintain Consistent Nutrition: Consume adequate protein (0.8-1g per pound bodyweight) and overall calories to support muscle protein synthesis and energy for training
- Use Appropriate Rep Ranges: Train in 3-6 rep range for maximum strength, 6-12 for strength-size combo, allowing specific adaptation to occur
- Plan Deload Weeks: Reduce training intensity by 40-60% every 4-6 weeks to allow recovery and prevent overreaching or plateau development
- Track Progress Systematically: Keep detailed logs of weights, sets, reps, and RPE to identify patterns and plan logical progression sequences
- Consider Periodization: Use structured training phases focusing on different aspects (strength, power, endurance) to prevent staleness and promote continued adaptation
How to Lift Heavier Weights Faster?
Important Safety Note: “Faster” progression must be balanced against injury risk and sustainable development. Rushing strength gains often leads to plateaus, overuse injuries, and setbacks that ultimately slow progress. Smart acceleration focuses on optimizing training efficiency rather than simply adding weight aggressively without regard for recovery or technique quality.
- Optimize Training Frequency: Train each lift 2-3 times per week with appropriate intensity distribution rather than once weekly for faster skill acquisition
- Use Autoregulation: Adjust daily training loads based on how you feel using RPE scales, allowing higher intensity on good days while backing off when needed
- Implement Cluster Training: Break sets into smaller chunks with short rest periods, allowing higher total volume at heavier weights per session
- Focus on Speed of Movement: Train with lighter loads (50-70%) moving the bar as explosively as possible to improve rate of force development
- Prioritize Sleep and Recovery: Ensure 8+ hours quality sleep and manage stress levels, as these factors directly impact strength adaptation speed
- Address Mobility Limitations: Improve movement quality through targeted mobility work, allowing better positioning and force production in lifts
- Use Competition Timing: Plan training around specific testing dates or competitions to create focused preparation periods with clear progression targets
- Strategic Supplementation: Consider creatine monohydrate (3-5g daily) and adequate protein intake to support faster strength and recovery adaptations
- Mental Preparation: Practice visualization and confidence-building techniques to improve your ability to attempt and succeed with heavier weights
- Get Professional Coaching: Work with qualified coach to identify technique inefficiencies and programming adjustments that accelerate safe progression
Weight Lifting Regimen for Beginners
Beginner weightlifting programs should prioritize movement quality, consistency, and gradual strength development over impressive weights or complex programming. New lifters benefit from frequent practice of fundamental movement patterns with manageable loads. The focus should be establishing proper habits, building work capacity, and creating sustainable training routines.
12-Week Beginner Strength Program
| Week | Frequency | Focus | Squat | Bench Press | Deadlift | Overhead Press | Accessory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | 3x/week | Form Learning | 3×8 (bodyweight) | 3×8 (empty bar) | 3×5 (light weight) | 3×8 (empty bar) | Basic movements |
| 3-4 | 3x/week | Pattern Development | 3×8 (light weight) | 3×8 (add 5lbs) | 3×5 (add 10lbs) | 3×8 (add 5lbs) | Bodyweight exercises |
| 5-6 | 3x/week | Strength Building | 3×5 (progressive) | 3×5 (progressive) | 3×5 (progressive) | 3×5 (progressive) | Light accessories |
| 7-8 | 3x/week | Load Progression | 3×5 (+5lbs/week) | 3×5 (+2.5lbs/week) | 3×5 (+10lbs/week) | 3×5 (+2.5lbs/week) | Targeted weak points |
| 9-10 | 3x/week | Strength Focus | 5×3 (heavier) | 5×3 (heavier) | 5×3 (heavier) | 5×3 (heavier) | Supporting muscles |
| 11-12 | 3x/week | Testing Phase | Work to 3RM | Work to 3RM | Work to 3RM | Work to 3RM | Deload accessories |
Essential Beginner Guidelines
Week 1-4: Foundation Phase
- Focus exclusively on movement quality over weight lifted
- Use empty barbell or bodyweight to learn proper patterns
- Practice setup, execution, and safety procedures
- Build training habit and basic work capacity
Week 5-8: Progressive Loading
- Begin systematic weight increases when form is consistent
- Add weight only when all reps completed with good form
- Learn to recognize proper technique breakdown points
- Introduce basic accessory exercises for balance
Week 9-12: Strength Development
- Transition to strength-focused rep ranges and intensities
- Test progress with heavier weights and lower repetitions
- Develop confidence with more challenging loads
- Plan for intermediate program transition

Benefits of Learning How to Lift Heavier Weights
Understanding the benefits of learning how to lift heavier weights motivates consistent training while revealing why progressive strength development is essential for overall fitness and health. These advantages extend beyond simple muscle building to include functional improvements.
- Increased Muscle Mass: Learning how to lift heavier weights stimulates muscle protein synthesis and hypertrophy, leading to larger, stronger muscles that improve both appearance and functional capacity.
- Enhanced Bone Density: Progressive weight training strengthens bones by placing controlled stress on skeletal system, reducing risk of osteoporosis and fractures later in life.
- Improved Metabolic Rate: Building strength through heavier lifting increases resting metabolic rate, helping burn more calories throughout the day even when not exercising.
- Better Functional Strength: The ability to lift heavier weights translates directly to improved performance in daily activities like lifting heavy objects, moving furniture, or carrying groceries.
- Increased Confidence: Achieving new personal records in lifting builds mental toughness and self-confidence that extends beyond the gym into other life areas.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Greater strength from lifting heavier weights improves performance in sports and recreational activities that require power and force production.
- Injury Prevention: Stronger muscles, tendons, and ligaments developed through progressive lifting provide better protection against injuries during physical activities.
- Hormonal Benefits: Heavy lifting stimulates beneficial hormone production including testosterone and growth hormone, supporting muscle growth and overall health.
For comprehensive fitness development, explore calisthenics at home no equipment routines that complement weight training.
How to Lift Heavier Weights Bench Press?
Learning how to lift heavier weights bench press requires specific techniques and strategies that address the unique demands of this fundamental exercise. Bench press progression involves technical refinements and systematic training approaches.
- Setup and Positioning: Proper bench press setup is crucial for how to lift heavier weights bench press safely and effectively. Position yourself with tight upper back, feet planted firmly, and optimal grip width for your body structure.
- Breathing Technique: Master the breathing pattern for bench pressing heavier weights. Take a deep breath at the top, hold it during the descent and press, then exhale after completing the repetition.
- Bar Path Optimization: Understanding proper bar path helps you lift heavier weights bench press more efficiently. The bar should travel in a slight arc from chest to lockout position over your shoulders.
- Leg Drive Utilization: Incorporating leg drive into your bench press technique helps generate more force and stability. Push through your feet to create full-body tension that supports heavier lifting.
- Progressive Overload Application: Apply progressive overload principles specifically to bench press training. Gradually increase weight, vary rep ranges, and use assistance exercises to build pressing strength.
Understanding how to start calisthenics provides foundation knowledge for building the core strength that supports heavy bench pressing.
Do’s and Don’ts of Proper Technique for Lifting Heavier Weights
Mastering proper technique is fundamental to learning how to lift heavier weights safely and effectively. Understanding both correct practices and common mistakes helps you maximize strength gains while minimizing injury risk during your training sessions.
Lifting Heavier Weights – Do’s
- Maintain Neutral Spine: Keep your back in natural alignment throughout all lifting movements to protect your spine and ensure optimal force transfer when learning how to lift heavier weights.
- Engage Your Core: Actively brace your abdominal muscles before each lift to create internal stability and support for handling heavier loads safely and effectively.
- Use Full Range of Motion: Move through complete joint ranges to maximize muscle activation and strength development while building flexibility alongside your ability to lift heavier weights.
- Control the Weight: Lower weights slowly and deliberately to maintain tension and build strength in both lifting and lowering phases of each exercise.
- Breathe Properly: Take deep breaths before lifting, hold during the lift, and exhale after completion to maintain proper internal pressure and oxygen flow.
- Warm Up Thoroughly: Prepare your body with adequate warm-up exercises to increase muscle temperature and reduce injury risk before attempting heavier weights.
Lifting Heavier Weights – Don’ts
- Don’t Bounce or Use Momentum: Avoid using bouncing motions or momentum to move weights, as this reduces muscle engagement and increases injury risk during heavy lifting.
- Don’t Round Your Back: Never allow your back to round under load, especially during deadlifts and rows, as this places dangerous stress on your spine.
- Don’t Hold Your Breath: Avoid holding your breath throughout entire sets, as this can cause dangerous blood pressure spikes and reduce performance.
- Don’t Ignore Pain: Never train through sharp or unusual pain, as this often indicates injury that requires rest and possibly medical attention.
- Don’t Skip Progression: Avoid jumping to much heavier weights without proper progression, as this increases injury risk and limits long-term development.
- Don’t Train Alone for Max Efforts: Never attempt maximum lifts without proper spotters or safety equipment, especially in exercises like bench press and squats.
How to Increase the Weight You Lift?
Learning how to increase the weight you lift requires systematic progression that challenges your muscles beyond their current capacity while maintaining proper form and safety. The most effective approach involves adding small increments regularly, typically 2.5-5kg for upper body exercises and 5-10kg for lower body movements each week. Focus on mastering your current weight completely before advancing, ensuring you can perform all prescribed repetitions with perfect technique. Additionally, vary your rep ranges periodically, using higher reps with lighter weights to build muscle endurance and lower reps with heavier weights to develop maximum strength, creating a well-rounded approach to how to lift heavier weights.
Weight Lifting Tips for Beginners
Starting your journey to learn how to lift heavier weights requires understanding fundamental principles that ensure safe progression and optimal results. These essential tips provide the foundation for successful strength training and help beginners avoid common mistakes.
- Start with Bodyweight Exercises: Master basic movement patterns without added weight before progressing to external loads. This builds foundational strength and proper form.
- Focus on Form Over Weight: Perfect your technique with lighter weights before attempting to lift heavier weights. Good form prevents injury and ensures optimal muscle activation.
- Begin with Compound Movements: Prioritize exercises that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, such as squats, deadlifts, and presses, for maximum strength development.
- Progress Gradually: Increase weights slowly and consistently rather than making large jumps. Small, regular increases lead to better long-term results.
- Learn Proper Breathing: Master breathing techniques early in your training to support heavier lifts and maintain proper core stability throughout movements.
- Allow Adequate Recovery: Schedule rest days between training sessions to allow muscle recovery and adaptation that supports your ability to lift heavier weights.
- Keep a Training Log: Track your workouts to monitor progress and ensure consistent advancement in your quest to lift heavier weights safely.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider working with a qualified trainer initially to learn proper form and develop effective training programs.
Building core stability through exercises like learning how to do plank exercise provides essential foundation strength for heavier lifting.
For foundation strength building, explore bodyweight exercises for beginners to prepare your body for weight training.

What Do You Need to Start Weight Training?
Beginning your journey to learn how to lift heavier weights requires basic equipment and preparation that supports safe, effective training. Understanding essential requirements helps you start properly while avoiding unnecessary expenses or inadequate preparation.
| Item | Type | Cost | Purpose |
| Gym | Membership | ₹1,660 – ₹6,640/month | Equipment Access |
| Shoes | Athletic | ₹4,150 – ₹12,450 | Stability Support |
| Clothes | Workout | ₹2,490 – ₹8,300 | Movement Freedom |
| Water | Bottle | ₹830 – ₹2,490 | Hydration |
| Towel | Gym | ₹415 – ₹1,660 | Hygiene |
| Log | Training | ₹415 – ₹1,245 | Progress Track |
Weight Lifting Exercises for Beginners
Learning fundamental exercises is crucial for developing the ability to lift heavier weights safely and effectively. These basic movements form the foundation for all advanced strength training and provide the best starting point for beginners.
| Exercise | Type | Muscles | Difficulty |
| Squat | Lower | Legs/Glutes | Easy |
| Press | Upper | Chest/Arms | Easy |
| Row | Pull | Back/Arms | Easy |
| Dead | Full | Legs/Back | Medium |
| Lunge | Lower | Legs/Core | Easy |
| Pull | Upper | Back/Arms | Medium |
Weight Training Schedule
Establishing a consistent training schedule is essential for learning how to lift heavier weights through progressive adaptation and recovery. Proper scheduling balances training stimulus with adequate recovery time for optimal strength development.
| Day | Focus | Duration | Rest |
| Mon | Upper | 45-60min | 24hr |
| Tue | Lower | 45-60min | 24hr |
| Wed | Rest | – | – |
| Thu | Upper | 45-60min | 24hr |
| Fri | Lower | 45-60min | 48hr |
| Sat | Rest | – | – |
| Sun | Rest | – | – |
Common Mistakes That Prevent Lifting Heavier Weights
Avoiding common errors helps you maximize your progress in learning how to lift heavier weights while preventing plateaus and injuries. These mistakes can significantly limit your strength development and increase injury risk.
Avoiding common errors helps you maximize your progress in learning how to lift heavier weights while preventing plateaus and injuries. These mistakes can significantly limit your strength development and increase injury risk.
- Ego Lifting: Attempting weights beyond your current capacity with poor form compromises safety and limits long-term progress. Focus on gradual progression rather than impressive numbers.
- Inconsistent Training: Irregular workout schedules prevent consistent progression and muscle adaptation. Maintain regular training frequency to support continuous strength development.
- Neglecting Recovery: Insufficient rest between workouts prevents muscle recovery and strength adaptation. Allow adequate time for rest and regeneration between training sessions.
- Poor Nutrition: Inadequate calorie and protein intake limits muscle recovery and strength gains. Fuel your body properly to support the demands of heavy lifting training.
- Ignoring Weak Points: Failing to address muscle imbalances and weak links limits overall strength potential. Identify and strengthen weak areas that limit your lifting capacity.
- Inadequate Warm-Up: Jumping straight into heavy lifting without proper preparation increases injury risk and reduces performance. Always prepare your body for heavy training loads.

Training Programs for Lifting Heavier Weights
Structured training programs provide systematic approaches for how to lift heavier weights through planned progression and periodization. These programs address different aspects of strength development while preventing overtraining.
- Linear Progression Programs Start with linear progression programs that add weight consistently each session. These programs work well for beginners learning how to lift heavier weights systematically.
- Periodized Training Approaches Advanced lifters benefit from periodized programs that vary intensity and volume over time. These approaches prevent plateaus and optimize long-term strength development.
- Conjugate Method Training This advanced approach rotates exercises and intensities to address multiple strength qualities simultaneously while maintaining continuous progression.
- Block Periodization Focus on specific training qualities in dedicated blocks, such as strength, power, or hypertrophy, to maximize adaptations before moving to the next phase.
For comprehensive upper body development, consider calisthenics pull workout and back calisthenics exercises alongside weight training.
Building lower body strength through calisthenics leg exercises complements your weight training and helps you lift heavier weights more effectively.
Nutrition for Lifting Heavier Weights
Proper nutrition is fundamental for how to lift heavier weights successfully, providing energy for intense training sessions and nutrients for muscle recovery and growth. Strategic eating plans support maximum strength development.
- Caloric Requirements Adequate calorie intake supports the energy demands of heavy lifting training while providing surplus energy for muscle building and recovery processes.
- Protein Intake Sufficient protein consumption supports muscle protein synthesis and repair after intense training sessions. Aim for 1.6-2.2g per kg of body weight daily.
- Carbohydrate Timing Strategic carbohydrate intake provides energy for training while supporting recovery. Time carbs around workouts for optimal performance and glycogen replenishment.
- Hydration Strategy Proper hydration maintains performance during heavy lifting sessions while supporting muscle function and recovery processes.
Many fitness enthusiasts explore calisthenics for weight loss while building strength, creating comprehensive fitness programs.
Recovery Strategies for Heavy Lifting
Optimal recovery is essential for how to lift heavier weights consistently while preventing overtraining and injury. Strategic recovery approaches maximize adaptation while maintaining training quality.
- Sleep Optimization Quality sleep is crucial for strength adaptation and recovery from heavy training. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep to support muscle repair and nervous system recovery.
- Active Recovery Methods Light activity on rest days promotes blood flow and recovery without interfering with adaptation. Consider walking, gentle stretching, or light cardio.
- Stress Management Managing life stress supports recovery and strength development. High stress levels can impair muscle building and strength adaptations.
- Recovery Monitoring Track recovery markers like sleep quality, mood, and training performance to optimize rest periods and training intensity.
For targeted muscle development, explore calisthenics for triceps and forearm calisthenics exercises.
Mental Preparation for Heavy Lifting
Mental preparation significantly impacts your ability to lift heavier weights by overcoming psychological barriers and building confidence. Strong mindset development supports physical strength progression.
- Visualization Techniques Mental rehearsal of successful lifts builds confidence and neural pathways that support actual performance. Visualize perfect technique and successful completion.
- Breathing and Focus Controlled breathing and mental focus enhance performance during heavy attempts. Develop pre-lift routines that optimize mental state.
- Goal Setting Clear, specific strength goals provide motivation and direction for training progression. Set both short-term and long-term lifting targets that align with your journey to learn how to lift heavier weights systematically.
- Confidence Building Progressive success in training builds confidence for heavier attempts. Celebrate small victories and maintain positive self-talk.
Understanding calisthenics vs gymnastics can help you appreciate different approaches to strength development.
Safety Considerations for Heavy Lifting
Safety is paramount when learning how to lift heavier weights, requiring proper precautions and risk management strategies. These guidelines help prevent injuries while maximizing training effectiveness.
- Proper Spotting Always use qualified spotters when attempting maximum loads, especially in exercises like bench press and squats where failure can be dangerous.
- Equipment Inspection Regularly check equipment for wear and damage that could compromise safety during heavy lifting sessions.
- Progressive Loading Increase weights gradually rather than making large jumps that exceed your current capacity and increase injury risk. This systematic approach is fundamental to learning how to lift heavier weights safely over time.
- Form Before Weight Never compromise proper form for heavier weights. Maintain technique standards even as loads increase to ensure safe progression.
For those interested in different training approaches, understanding crossfit vs calisthenics provides valuable perspective.
Technology and Tools for Strength Training
Modern technology and tools can enhance your ability to lift heavier weights through better tracking, analysis, and programming. These resources support systematic progression and performance optimization.
- Training Apps Use smartphone apps to track workouts, monitor progression, and calculate optimal training loads for consistent advancement.
- Wearable Technology Heart rate monitors and fitness trackers provide valuable data about training intensity and recovery status.
- Video Analysis Recording lifts allows detailed technique analysis and identification of areas for improvement in your lifting form.
- Load Progression Calculators Mathematical tools help plan systematic weight increases and predict realistic strength goals based on current performance.
For additional cardio training that complements strength work, learn how to do jumping jacks and how many jumping jacks to burn 500 calories.
Conclusion
Learning how to lift heavier weights requires systematic application of progressive overload principles, proper technique, adequate recovery, and consistent training. Success in how to lift heavier weights comes from patience, dedication to proper form, and understanding that strength development is a gradual process that rewards consistency over time.
Advanced practitioners might explore complex movements like calisthenics planche for comprehensive strength development.
Want to master the calisthenics handstand and take your skills to the next level? Whether you’re a beginner or pushing advanced skills, ISC – Indian School of Calisthenics offers expert guidance to help you master bodyweight training. Visit us at SRPF Ground, NH8, Goregaon (E), Mumbai – 400065. For class schedules, personalized coaching, or more details, call +91 77159 53218. Train smart, move better, and unlock your back strength with ISC.
How to Lift Heavier Weights? – FAQs
How can I lift heavier weights?
Focus on progressive overload, maintain proper form, ensure adequate rest between sets, eat sufficient protein, and follow a structured training program consistently.
What is the 5 4 3 2 1 method of lifting?
This method involves performing 5 reps at moderate weight, then 4, 3, 2, and finally 1 rep while increasing weight each set to build strength.
How to increase strength to lift more weight?
Increase strength through progressive overload, compound exercises, consistent training frequency, proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and addressing weak points in your lifts.
Why can’t I lift heavier weights?
Common reasons include inadequate recovery, poor nutrition, inconsistent training, technical issues, mental barriers, or reaching a natural plateau requiring program changes.
What is the best way to increase weights?
Increase weights gradually by 2.5-5kg per week for upper body and 5-10kg for lower body exercises while maintaining proper form and technique.
Is it better to lift heavy or light?
Both have benefits – heavy weights (1-6 reps) build maximum strength, while lighter weights (8-15 reps) promote muscle growth and endurance.
What is the 2 for 2 rule?
If you can perform 2 extra reps beyond your target reps for 2 consecutive workouts, increase the weight by 2-10% for your next session.
How to lift heavy correctly?
Maintain proper form, warm up thoroughly, use controlled movements, breathe correctly, engage core muscles, and never sacrifice technique for heavier weight.
Why exhale when lifting weights?
Exhaling during the exertion phase helps stabilize core pressure, maintain proper breathing patterns, and prevent excessive blood pressure spikes during heavy lifting.
Do slow reps build more muscle?
Slower reps can build muscle by increasing time under tension, but moderate tempo with full range of motion typically provides optimal results for both strength and size.