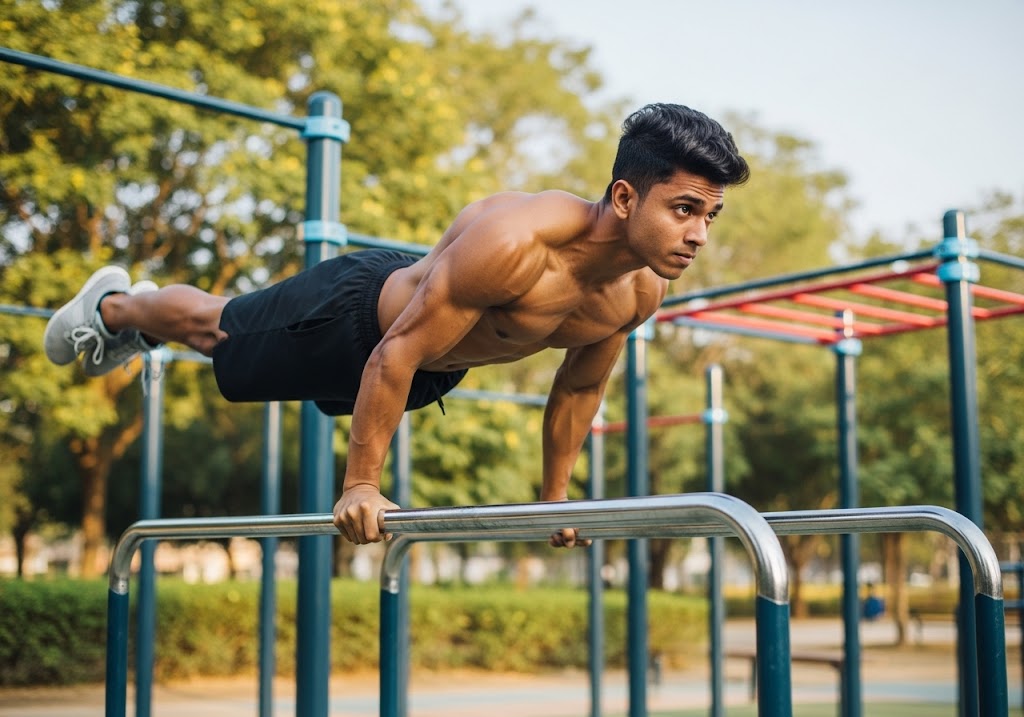
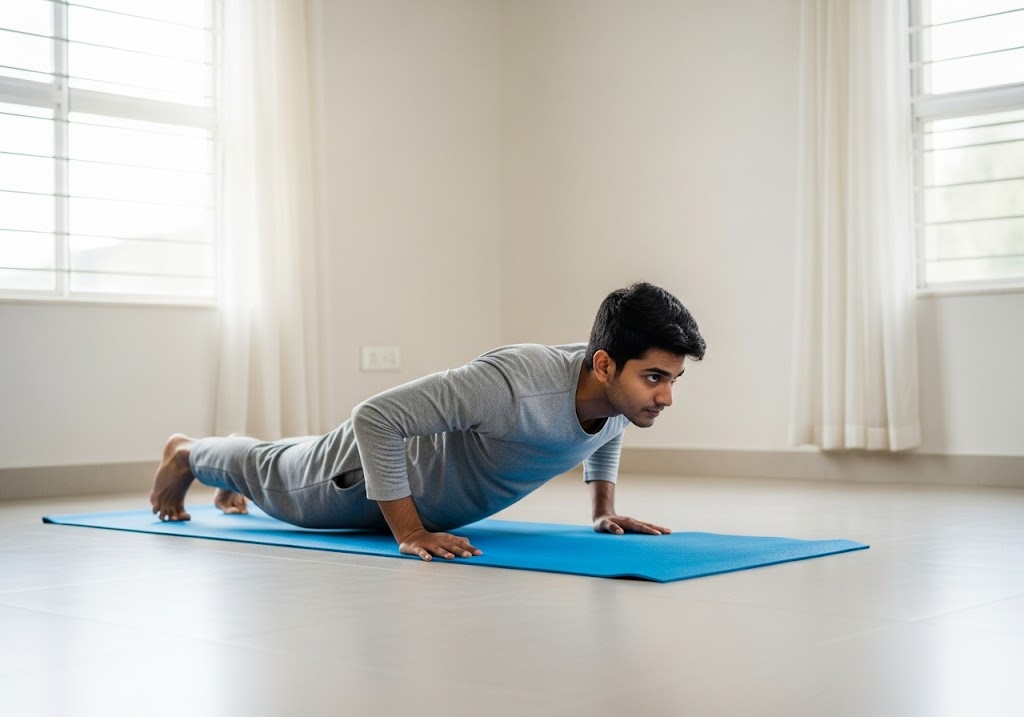
Unilateral exercises involve one limb at a time (like single-leg squats or one-arm rows), while bilateral exercises involve both limbs simultaneously (like regular squats or bench press). Unilateral exercises are beneficial for improving balance and addressing muscle imbalances between sides, whereas bilateral exercises are used for building maximum strength and muscle mass through heavier loading capacity.
Want to understand the critical differences between unilateral VS bilateral training for maximum workout effectiveness? Both training approaches offer unique benefits that can transform your fitness results when used strategically. This complete comparison reveals when and how to use each approach for optimal strength, balance, and muscle development.
Understanding unilateral vs bilateral movements helps create balanced training programs that address weaknesses while building maximum strength. Whether you’re correcting imbalances through single-limb exercises or building raw power through bilateral movements, this comprehensive comparison covers everything you need to know about these fundamental training approaches.
Table of Contents
What is Unilateral Training?
Unilateral training focuses on working one limb or side of your body at a time, creating unique challenges that bilateral exercises cannot provide. This approach forces each side to work independently, revealing strength imbalances and coordination issues while building functional strength patterns that transfer to real-world activities and athletic performance.
The core principle behind unilateral VS bilateral training differences lies in how your nervous system adapts to single-limb challenges. When performing unilateral exercises, your core works overtime to maintain stability while the working limb generates force independently. This creates superior balance, coordination, and proprioceptive awareness compared to bilateral movements in unilateral VS bilateral training comparison.
Common unilateral exercises include single-leg squats, one-arm rows, lunges, and single-arm presses. These movements challenge stability, reveal weaknesses, and build functional strength that improves daily activities and reduces injury risk through balanced development across both sides of your body in effective unilateral VS bilateral training programs.
For comprehensive single-limb training options, exploring calisthenics exercises provides excellent bodyweight alternatives for unilateral development.
What is Bilateral Training?
Bilateral training involves using both limbs simultaneously to generate maximum force and build overall strength efficiently. This traditional approach allows for heavier loading and greater muscle mass development while requiring less balance and coordination compared to unilateral alternatives in the unilateral VS bilateral training comparison.
The primary advantage of bilateral training lies in its ability to overload muscles with heavy resistance while maintaining stability through dual-limb support. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench press allow you to lift significantly more weight than their unilateral counterparts, creating greater mechanical tension for muscle growth.
Bilateral movements form the foundation of most strength training programs due to their efficiency and effectiveness for building raw power and muscle mass. These exercises work multiple muscle groups simultaneously while allowing progressive overload through increased weight, making them essential for strength development goals.
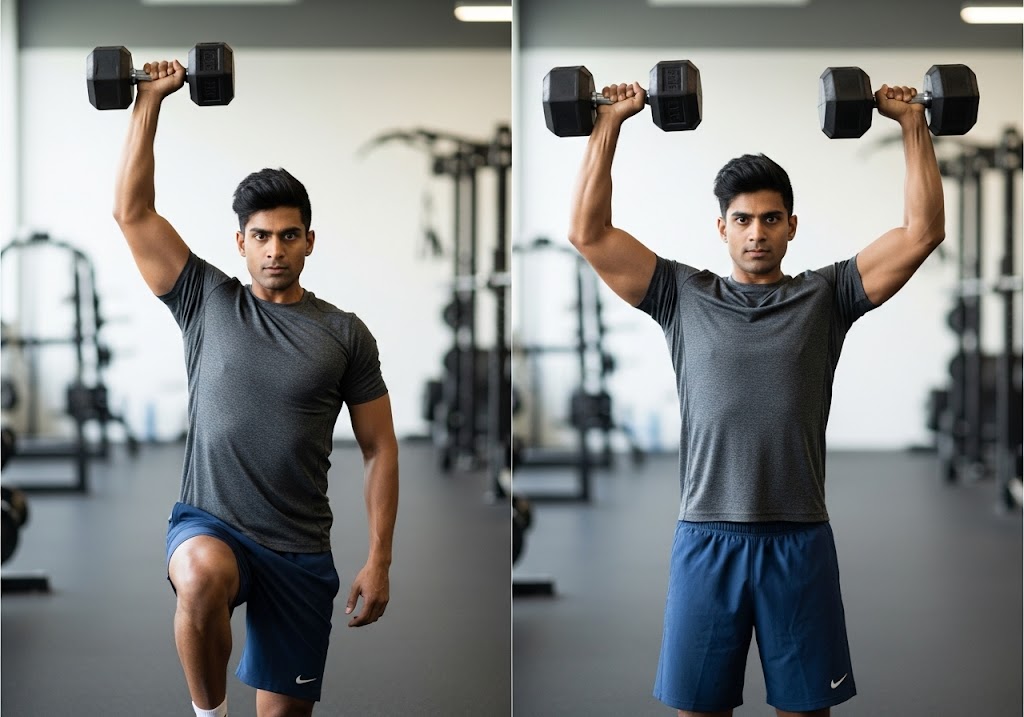

Difference Between Unilateral and Bilateral Exercises
The fundamental difference between unilateral and bilateral exercises extends beyond simply using one limb versus two. These training approaches create distinctly different physiological demands, neural adaptations, and strength development patterns that serve different purposes in comprehensive fitness programs.
| Aspect | Unilateral Exercises | Bilateral Exercises | Impact on Training |
| Limb Usage | One arm or leg at a time | Both limbs simultaneously | Training specificity |
| Load Capacity | Lower weight potential | Higher weight capacity | Strength development |
| Balance Demand | High stability challenge | Stable base of support | Coordination improvement |
| Core Activation | Maximum engagement | Moderate involvement | Functional strength |
| Imbalance Detection | Reveals weaknesses | May mask imbalances | Corrective potential |
| Training Time | Longer duration needed | Time efficient | Workout planning |
| Skill Requirement | Higher coordination | Lower complexity | Learning curve |
| Muscle Activation | Independent limb work | Synchronized movement | Motor pattern development |
The difference between unilateral and bilateral exercises becomes apparent when examining how each approach challenges your body’s systems. Unilateral movements demand greater neuromuscular control and proprioceptive awareness, while bilateral exercises allow for maximum force production through coordinated dual-limb effort.
Training specificity also differs significantly in unilateral VS bilateral training applications. Unilateral exercises better prepare you for real-world activities that often require single-limb stability and strength, while bilateral movements excel at building overall strength and muscle mass through heavy loading patterns.
For targeted core development that supports both training types, calisthenics ab workout provides essential stability training for optimal performance.
Unilateral vs Bilateral Movements
Understanding unilateral vs bilateral movements helps optimize exercise selection based on specific training goals and individual needs. Each movement pattern offers unique advantages that complement each other when integrated strategically into comprehensive unilateral VS bilateral training programs for maximum effectiveness and balanced development.
| Movement Aspect | Unilateral Movements | Bilateral Movements | Training Impact |
| Stability Demand | High balance challenge | Stable base support | Coordination vs Power |
| Muscle Activation | Independent limb work | Synchronized activation | Imbalance detection vs Efficiency |
| Neural Complexity | High coordination needs | Lower skill requirements | Learning curve differences |
| Force Production | Limited by stability | Maximum force potential | Functional vs Absolute strength |
| Movement Patterns | Real-world specificity | Gym-specific patterns | Daily life vs Athletic performance |
| Progressive Overload | Balance/coordination focus | Weight-based progression | Skill vs Load advancement |
| Training Time | Longer duration needed | Time-efficient execution | Workout planning considerations |
| Injury Risk | Lower impact forces | Higher loading stress | Safety profile differences |

Bilateral vs Unilateral Strength Training
Bilateral vs unilateral strength training approaches serve different purposes in comprehensive fitness programs, with each method offering distinct advantages for strength development, muscle building, and functional improvement. Understanding when to emphasize each approach optimizes training results and prevents plateau effects.
Strength gains manifest differently between bilateral and unilateral training methods. Bilateral exercises allow for maximum loading and create greater mechanical tension, leading to superior absolute strength development. Unilateral exercises build functional strength through improved balance, coordination, and individual limb capacity development.
| Training Aspect | Bilateral Strength Training | Unilateral Strength Training | Best Application |
| Load Capacity | Maximum weight potential | Limited by stability | Raw strength building |
| Muscle Mass | Superior hypertrophy | Moderate muscle building | Bodybuilding goals |
| Functional Strength | Limited carryover | Excellent real-world transfer | Athletic performance |
| Balance Training | Minimal improvement | Significant enhancement | Injury prevention |
| Time Efficiency | High efficiency | Lower efficiency | Busy schedules |
| Imbalance Correction | Poor detection | Excellent correction | Rehabilitation |
| Power Development | Maximum power output | Unilateral power | Sport-specific needs |
| Coordination | Basic requirements | Advanced demands | Skill development |
The bilateral vs unilateral strength training decision depends on your primary goals and current fitness level. Beginners often benefit from bilateral movements to build foundational strength, while advanced athletes may emphasize unilateral training for sport-specific adaptations and imbalance correction.
For comprehensive strength development that combines both approaches, compound dumbbell exercises provides excellent options for integrated training programs.
Pros and Cons of Unilateral Training
Understanding the pros and cons of unilateral training helps determine when this approach best serves your fitness goals and training needs. While unilateral exercises offer unique benefits, they also present specific challenges that must be considered in program design and implementation.
Pros of Unilateral Training
Unilateral training excels at addressing muscular imbalances that bilateral exercises often mask or even perpetuate. This training approach forces each side of your body to work independently, revealing strength differences and allowing targeted correction of weaknesses that could lead to injury or performance limitations.
- Imbalance Correction: Identifies and fixes strength differences between left and right sides that bilateral training cannot address effectively
- Enhanced Core Stability: Forces deep stabilizing muscles to work harder, building functional core strength for real-world activities
- Improved Balance and Coordination: Challenges proprioception and single-limb stability, enhancing overall movement quality and athletic performance
- Functional Movement Patterns: Mirrors many daily activities and sports movements that require single-limb strength and stability
- Injury Prevention: Addresses weaknesses and compensations that commonly lead to overuse injuries and movement dysfunctions
- Increased Training Variety: Provides fresh challenges and prevents adaptation plateaus that occur with repetitive bilateral movements
Cons of Unilateral Training
Despite its benefits, unilateral training presents certain limitations that must be considered when designing comprehensive fitness programs. These challenges often require strategic programming and patience to overcome effectively.
- Lower Load Capacity: Cannot handle as much weight as bilateral exercises, limiting maximum strength development potential
- Time Inefficiency: Requires double the time since each side must be trained separately, making workouts longer
- Higher Skill Demand: Requires greater balance and coordination, creating a steeper learning curve for beginners
- Fatigue Accumulation: Core and stabilizing muscles fatigue quickly, potentially limiting training volume and intensity
- Limited Muscle Building: Lower loads may not provide optimal stimulus for maximum muscle hypertrophy compared to bilateral training
- Complexity Issues: More complex movement patterns may be difficult for those with balance or coordination limitations
For building strength that supports unilateral training, best workout to lose weight and gain muscle includes balanced approaches for comprehensive development.
Pros and Cons of Bilateral Training
Examining the pros and cons of bilateral training reveals why this approach forms the foundation of most strength training programs while also highlighting areas where unilateral training may provide superior benefits in the unilateral VS bilateral training comparison.
Pros of Bilateral Training
Bilateral training offers significant advantages for building raw strength, muscle mass, and power through its ability to handle heavy loads with stable support. This approach provides efficient muscle building and strength development that forms the foundation for advanced training progressions in unilateral VS bilateral training programs.
- Maximum Load Capacity: Allows for heaviest possible weights, creating optimal mechanical tension for strength and muscle development
- Time Efficiency: Works both sides simultaneously, making workouts shorter and more time-effective for busy schedules
- Superior Muscle Building: Heavy loads provide excellent stimulus for muscle hypertrophy and overall mass development
- Power Development: Enables maximum force production through coordinated dual-limb effort for athletic performance
- Easier Learning Curve: More stable and predictable movement patterns make exercises easier to learn and master
- Progressive Overload: Simple progression through increased weight makes strength gains straightforward to achieve
- Mental Confidence: Heavy lifting builds psychological confidence and satisfaction from moving substantial weights
- Metabolic Demands: Large muscle group involvement creates significant caloric expenditure and metabolic benefits
For mastering proper form in fundamental bilateral movements, how to do a perfect squat provides essential technique guidance for safe and effective training.
Cons of Bilateral Training
While bilateral training excels in many areas, it has notable limitations that unilateral training can address more effectively. Understanding these weaknesses helps create more balanced and comprehensive training programs.
- Imbalance Masking: Stronger side compensates for weaker side, hiding imbalances that may lead to injury over time
- Limited Functional Transfer: May not translate well to real-world activities that require single-limb strength and stability
- Reduced Core Challenge: Stable base reduces core stabilization demands compared to unilateral exercise challenges
- Balance Limitations: Provides minimal balance and proprioceptive training benefits for overall movement quality
- Plateau Potential: Body adapts quickly to predictable movement patterns, potentially limiting long-term progress
- Overuse Risk: Repetitive bilateral patterns may contribute to overuse injuries without addressing underlying imbalances

Unilateral vs Bilateral Benefits
Comparing unilateral vs bilateral benefits reveals that both training approaches offer unique advantages that complement each other in well-designed fitness programs. Understanding these benefits helps determine the optimal balance between training methods based on individual goals and needs.
The benefits of each training approach in unilateral VS bilateral training comparison depend largely on your specific goals, experience level, and current physical condition. Neither approach is universally superior; instead, they serve different purposes and work synergistically when combined strategically.
| Benefit Category | Unilateral Benefits | Bilateral Benefits | Best Choice |
| Strength Building | Functional, balanced strength | Maximum absolute strength | Depends on goals |
| Muscle Development | Balanced, proportional growth | Maximum muscle mass | Bilateral for size |
| Athletic Performance | Sport-specific movements | Power and force production | Sport-dependent |
| Injury Prevention | Imbalance correction | Strong foundation | Unilateral focus |
| Time Efficiency | Lower efficiency | Higher efficiency | Bilateral wins |
| Balance Training | Excellent improvement | Minimal benefit | Unilateral clear winner |
| Core Strength | Maximum engagement | Moderate activation | Unilateral superior |
| Load Progression | Complex progression | Simple weight increases | Bilateral easier |
| Beginner Friendly | Higher learning curve | Easier to master | Bilateral better |
| Advanced Training | Addresses weaknesses | Builds maximum strength | Both important |
The optimal approach in unilateral vs bilateral benefits consideration involves strategically combining both methods rather than choosing one exclusively. This integrated approach maximizes the unique advantages of each training style while minimizing their individual limitations.
For comprehensive upper body development using both approaches, calisthenics chest exercises provides excellent examples of integrated training methods.

When to Use Unilateral Training?
Determining when to use unilateral training in your unilateral VS bilateral training program depends on specific goals, current weaknesses, and training phase. Certain situations and conditions make unilateral exercises particularly beneficial for optimal results and balanced development.
Unilateral training becomes essential when addressing muscular imbalances that bilateral exercises cannot correct effectively in unilateral VS bilateral training programs. If you notice strength differences between sides, coordination issues, or recurring injuries on one side of your body, unilateral exercises should take priority in your training program.
Rehabilitation and injury prevention phases benefit significantly from unilateral training emphasis in unilateral VS bilateral training approaches. Physical therapists often prescribe single-limb exercises to restore balance, rebuild strength after injury, and prevent future problems through improved movement patterns and bilateral strength balance.
Athletes in sports requiring single-limb strength and stability should prioritize unilateral training during sport-specific preparation phases. Sports like tennis, baseball, martial arts, and running demand unilateral strength that bilateral training alone cannot adequately develop in comprehensive unilateral VS bilateral training programs.
For a complete guide to single-limb movements and their applications, unilateral exercises provides detailed instructions and progressions for balanced development.
For pull-up variations that demonstrate unilateral progression, calisthenics close grip pull ups and calisthenics wide grip pull ups show excellent single-arm progressions.
When to Use Bilateral Training?
Bilateral training should dominate your program when maximum strength development and muscle building are primary goals. The superior loading capacity of bilateral exercises makes them irreplaceable for building foundational strength and substantial muscle mass through progressive overload principles.
Beginners should emphasize bilateral training initially to develop basic movement patterns, build strength reserves, and create a solid foundation before progressing to more challenging unilateral exercises. This approach ensures proper development and reduces injury risk during the learning phase.
Time-constrained training periods benefit from bilateral exercise emphasis due to their superior efficiency. When training time is limited, bilateral movements provide maximum training stimulus in minimal time, making them ideal for maintaining fitness during busy periods.
Power development phases require bilateral training focus to achieve maximum force production through coordinated dual-limb effort. Athletes needing explosive power for jumping, throwing, or lifting benefit from bilateral exercise emphasis during specific training cycles.
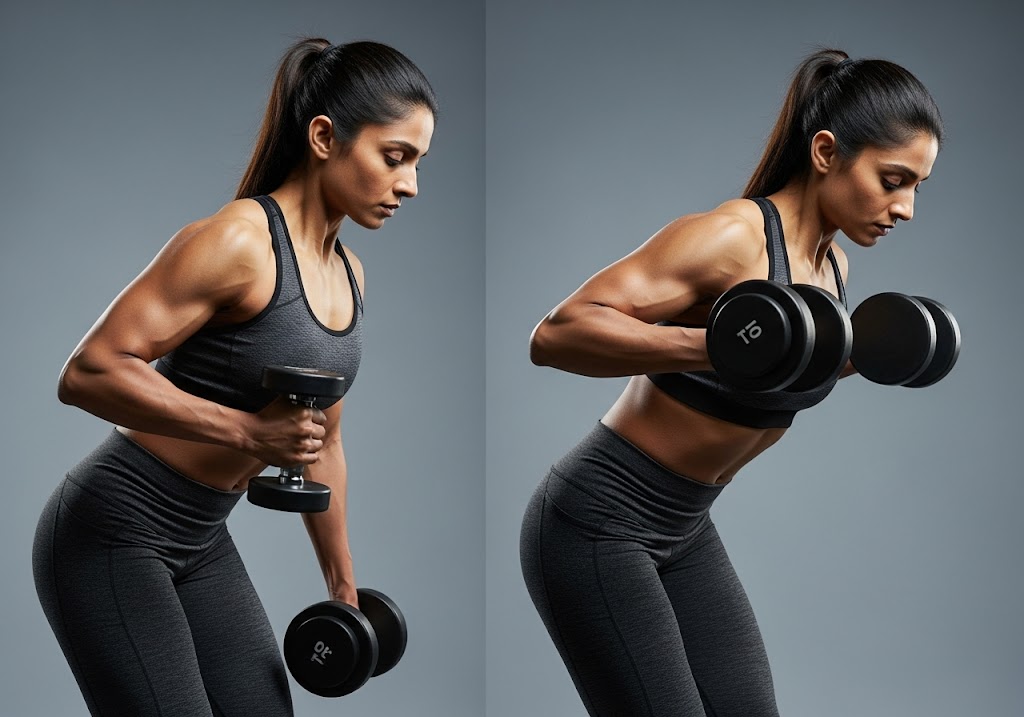
Sample Unilateral vs Bilateral Workout Comparison
This side-by-side workout comparison demonstrates how unilateral VS bilateral training approaches create different training stimuli and serve distinct purposes in comprehensive fitness programs. Both workouts target the same muscle groups but through different methodologies and training demands.
| Exercise Type | Unilateral Workout | Bilateral Workout | Training Focus |
| Lower Body | Single-leg squats (3×8 each) | Back squats (4×8) | Balance vs Power |
| Upper Pull | Single-arm rows (3×10 each) | Bent-over rows (4×8) | Stability vs Load |
| Upper Push | Single-arm press (3×8 each) | Bench press (4×8) | Core vs Strength |
| Hip Hinge | Single-leg deadlift (3×6 each) | Deadlifts (4×6) | Balance vs Maximum |
| Core | Side planks (3x30s each) | Planks (3x60s) | Unilateral vs Total |
| Total Time | 45-60 minutes | 30-40 minutes | Longer vs Efficient |
The unilateral workout emphasizes balance, coordination, and imbalance correction while requiring more time and concentration. The bilateral workout focuses on maximum strength development and muscle building through heavier loading in less time.
For comprehensive leg training that combines both approaches, calisthenics leg exercises provides excellent examples of integrated lower body training.
How to Combine Unilateral and Bilateral Training?
Successfully combining unilateral and bilateral training maximizes the benefits of both approaches while minimizing their individual limitations. Strategic integration creates comprehensive programs that build strength, correct imbalances, and improve overall function through complementary training methods.
The most effective approach to unilateral VS bilateral training integration involves periodizing emphasis based on training phases and specific goals. Base building phases may emphasize bilateral training for strength development, while corrective phases focus on unilateral exercises for balance and imbalance resolution in systematic unilateral VS bilateral training progression.
| Integration Method | Approach | Example | Benefits |
| Session Split | Alternate workout focus | Monday bilateral, Wednesday unilateral | Dedicated attention |
| Exercise Pairing | Combine in same workout | Bilateral squat + unilateral lunge | Comprehensive stimulus |
| Phase Periodization | Emphasize by training block | 4 weeks bilateral, 2 weeks unilateral | Systematic development |
| Superset Method | Back-to-back exercises | Bilateral press → single-arm press | Time efficiency |
| Assessment Based | Address current needs | Test imbalances, adjust accordingly | Individualized approach |
The key to successful integration lies in understanding your current needs and systematically addressing weaknesses while maintaining strengths. Regular assessment of imbalances and movement quality guides the optimal balance between training approaches in effective unilateral VS bilateral training programs.
For advanced bodyweight challenges that combine both approaches, calisthenics handstand demonstrates ultimate unilateral upper body development.
Which is Better: Unilateral or Bilateral Training?
The question of which is better in unilateral VS bilateral training has no universal answer, as superiority depends entirely on individual goals, current fitness level, and specific needs. Both approaches offer irreplaceable benefits that work synergistically rather than competitively in optimal training programs.
| Training Goal | Better Choice | Reason | Application |
| Maximum Strength | Bilateral Training | Higher load capacity allows greater force development | Powerlifting, strength sports |
| Muscle Building | Bilateral Training | Heavier weights create optimal hypertrophy stimulus | Bodybuilding goals |
| Balance Improvement | Unilateral Training | Single-limb challenges enhance proprioception | Injury prevention, elderly |
| Imbalance Correction | Unilateral Training | Reveals and addresses side-to-side differences | Rehabilitation, athletes |
| Time Efficiency | Bilateral Training | Works both sides simultaneously | Busy schedules |
| Functional Strength | Unilateral Training | Mirrors real-world single-limb demands | Daily activities, sports |
| Power Development | Bilateral Training | Maximum force production through dual-limb coordination | Athletic performance |
| Core Stability | Unilateral Training | Anti-rotation challenges build deeper core strength | Functional fitness |
| Beginner Training | Bilateral Training | Easier to learn and master movement patterns | Fitness newcomers |
| Advanced Training | Both Approaches | Addresses all aspects of strength and function | Experienced athletes |
For building the core strength that supports both training types, how to get a six pack quick provides essential abdominal training that enhances all movement patterns.
Common Mistakes in Unilateral VS Bilateral Training
Avoiding common mistakes in unilateral VS bilateral training ensures optimal results while preventing frustration and potential injuries. Many people make these errors without realizing their impact on training effectiveness and long-term progress toward fitness goals.
The most frequent mistake involves choosing one approach exclusively instead of integrating both methods strategically. This limitation prevents you from gaining the unique benefits that each training style offers, ultimately limiting overall development and functional capacity.
- All-or-Nothing Mentality: Using only unilateral or only bilateral exercises instead of strategic combination for complete development
- Ignoring Imbalances: Continuing bilateral training when significant imbalances exist that require unilateral correction first
- Poor Progression: Advancing too quickly in unilateral exercises without adequate balance and stability development
- Time Mismanagement: Not accounting for increased time requirements when incorporating more unilateral exercises into programs
- Goal Misalignment: Using unilateral training for maximum strength goals or bilateral training for balance improvement
- Inadequate Assessment: Failing to regularly evaluate imbalances and adjust training emphasis accordingly
Understanding these mistakes helps create more effective programs that leverage the strengths of both training approaches while avoiding common pitfalls that limit progress.
For comprehensive back development using both approaches, how to get a wider back demonstrates integrated training for optimal results.
Conclusion
The unilateral VS bilateral training debate isn’t about choosing one approach over the other, but rather understanding how to use both methods strategically for optimal results. Bilateral training excels at building maximum strength and muscle mass through heavy loading, while unilateral training addresses imbalances, improves balance, and builds functional strength patterns. The most effective unilateral VS bilateral training programs combine both approaches based on individual goals, current weaknesses, and specific needs for comprehensive fitness development that transfers to real-world activities and athletic performance.
Want to master the calisthenics handstand and take your skills to the next level? Whether you’re a beginner or pushing advanced skills, ISC – Indian School of Calisthenics offers expert guidance to help you master bodyweight training. Visit us at SRPF Ground, NH8, Goregaon (E), Mumbai – 400065. For class schedules, personalized coaching, or more details, call +91 77159 53218. Train smart, move better, and unlock your back strength with ISC.
Unilateral VS Bilateral Training – FAQs
What is the difference between unilateral and bilateral exercises?
Unilateral exercises work one limb at a time while bilateral exercises use both limbs simultaneously, creating different stability demands and strength development patterns.
Which is better: unilateral or bilateral training?
Neither is universally better; bilateral training builds maximum strength while unilateral training improves balance and corrects imbalances – both are essential.
What are the benefits of unilateral training?
Unilateral training corrects imbalances, improves balance and coordination, enhances core stability, and builds functional strength for real-world activities.
Should beginners do unilateral or bilateral exercises?
Beginners should emphasize bilateral exercises initially to build foundational strength, then gradually incorporate unilateral exercises for balance and coordination.
How do you combine unilateral and bilateral training?
Combine both by alternating focus between workouts, pairing exercises in sessions, or periodizing emphasis based on training phases and goals.
What are examples of unilateral exercises?
Common unilateral exercises include single-leg squats, one-arm rows, lunges, single-arm presses, and side planks that work one side independently.
What are examples of bilateral exercises?
Bilateral exercises include squats, deadlifts, bench press, pull-ups, and planks where both limbs work together simultaneously.
When should you use unilateral training?
Use unilateral training when correcting imbalances, during rehabilitation, for sport-specific preparation, or when balance and coordination need improvement.
Can unilateral training replace bilateral training?
Unilateral training cannot fully replace bilateral training as it cannot provide the same heavy loading stimulus needed for maximum strength development.