How many calories does 45 minutes of HIIT burn? A 45-minute HIIT workout typically burns 375-600 calories, depending on your body weight, workout intensity, and fitness level.
High-intensity interval training has become one of the most popular workout methods for burning calories and losing weight quickly. Many people choose HIIT because it delivers impressive results in shorter time periods compared to traditional cardio exercises. Understanding exactly how many calories you burn during different workout durations helps you plan effective fitness routines and achieve your weight loss goals faster.
The calorie burn from HIIT workouts depends on several important factors including your current weight, workout intensity level, specific exercises performed, and your overall fitness condition. Unlike steady-state cardio, HIIT continues burning calories even after your workout ends through a process called excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). This afterburn effect makes HIIT particularly effective for people looking to maximize their calorie burn in limited time.
Table of Contents
Understanding HIIT Calorie Burn in 45 Minutes
HIIT workouts create significant calorie burn through alternating periods of maximum effort and recovery phases. During a 45-minute session, your body works harder than traditional steady-state cardio, resulting in higher immediate calorie expenditure. The intensity level during work intervals typically reaches 80-95% of your maximum heart rate, creating substantial energy demands on your cardiovascular and muscular systems.
Research shows that how many calories does 45 minutes of HIIT burn ranges from 375-600 calories for most individuals. However, some highly intense workouts can burn up to 800-1000 calories per session for very fit individuals performing at maximum capacity. The variation depends primarily on body weight, with heavier individuals typically burning more calories than lighter ones during identical workouts.
| Body Weight | Calories Burned (45 min) | Intensity Level |
|---|---|---|
| 55 kg | 320-450 calories | Moderate-High |
| 65 kg | 375-525 calories | Moderate-High |
| 75 kg | 430-600 calories | Moderate-High |
| 85 kg | 485-675 calories | Moderate-High |
| 95 kg | 540-750 calories | Moderate-High |
The metabolic equivalent of task (MET) value for HIIT typically ranges between 8-18, depending on exercise selection and intensity level. This means HIIT burns 8-18 times more energy than resting metabolism, explaining why these workouts are so effective for weight management and cardiovascular fitness improvements.
Lunge or split squat-which burns more? split squat vs lunge
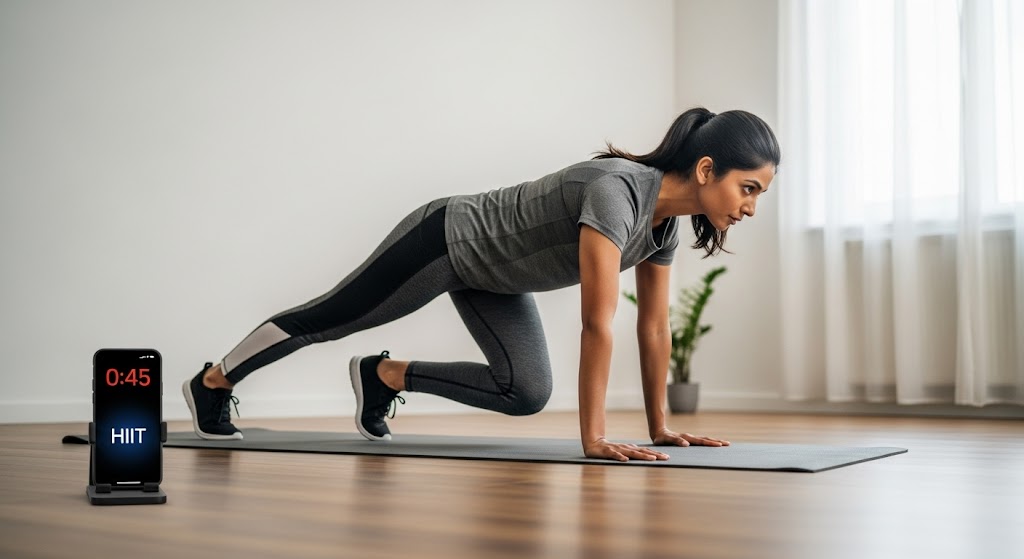

How Many Calories Does 45 Minutes of HIIT Burn? – Sample Workout
A 45-minute HIIT workout typically burns 400-650 calories depending on body weight, exercise intensity, and fitness level. High-intensity interval training combines short bursts of maximum effort with brief recovery periods, creating exceptional calorie burn during and after exercise through EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption) for continued metabolic benefits.
45-Minute HIIT Workout Structure
Total Workout Time: 45 minutes
Warm-up: 5 minutes
Main Workout: 35 minutes (7 rounds × 5 minutes each)
Cool-down: 5 minutes
Work-to-Rest Ratio: 45 seconds work, 15 seconds rest
Estimated Calorie Burn: 400-650 calories
HIIT Exercise Overview
| Sr.No. | Exercise | Primary Target | Difficulty | Equipment | Calories/Minute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Burpees | Full Body | Advanced | None | 12-15 |
| 2 | Mountain Climbers | Core, Cardio | Intermediate | None | 10-12 |
| 3 | Jump Squats | Lower Body | Intermediate | None | 10-13 |
| 4 | High Knees | Cardio, Legs | Beginner | None | 8-10 |
| 5 | Push-up to T | Upper Body, Core | Intermediate | None | 9-12 |
| 6 | Plank Jacks | Core, Shoulders | Intermediate | None | 8-11 |
| 7 | Jumping Lunges | Lower Body | Intermediate | None | 10-13 |
| 8 | Bear Crawl | Full Body | Advanced | None | 11-14 |
| 9 | Tuck Jumps | Lower Body, Power | Advanced | None | 12-15 |
| 10 | Russian Twists | Core, Obliques | Beginner | None | 6-8 |
Detailed Exercise Instructions
1. Burpees
Burpees represent the ultimate full-body HIIT exercise, combining strength, cardio, and explosive power in one demanding movement. This exercise engages every major muscle group while elevating heart rate to maximum levels, creating exceptional calorie burn and metabolic conditioning. The compound nature makes burpees incredibly efficient for burning calories while building functional strength and cardiovascular endurance throughout the entire body.
How to Do Burpees?
- Start standing, squat down and place hands on floor, jump feet back to plank position
- Perform one push-up, jump feet back to squat, then explosively jump up with arms overhead
- Land softly and immediately begin next repetition, maintaining rapid pace throughout set
2. Mountain Climbers
Mountain climbers provide intense core training while delivering exceptional cardiovascular conditioning through rapid alternating leg movements. This dynamic exercise targets the core, shoulders, and legs simultaneously while maintaining elevated heart rate for maximum calorie burn. The sustained plank position combined with explosive leg movement creates perfect conditions for HIIT training while building functional strength and endurance.
How to Do Mountain Climbers?
- Start in high plank position with hands under shoulders, body in straight line
- Rapidly alternate driving knees toward chest while maintaining stable plank position
- Keep core engaged and avoid bouncing hips, focusing on controlled explosive movement
3. Jump Squats
Jump squats transform the basic squat into an explosive plyometric exercise that maximizes lower body power and calorie burn during HIIT sessions. This exercise develops fast-twitch muscle fibers while providing intense cardiovascular conditioning through continuous explosive movements. The combination of strength training and plyometric power makes jump squats exceptionally effective for building athletic performance while torching calories.
How to Do Jump Squats?
- Start in squat position with feet shoulder-width apart, arms at sides or crossed
- Explosively jump up as high as possible while extending arms overhead
- Land softly back into squat position and immediately prepare for next explosive jump
4. High Knees
High knees deliver exceptional cardiovascular training while targeting hip flexors and quadriceps through rapid leg cycling movements. This exercise elevates heart rate quickly while improving running mechanics and leg strength, making it perfect for HIIT warm-ups or high-intensity intervals. The simple movement pattern allows maximum effort while building speed, agility, and cardiovascular endurance essential for athletic performance.
How to Do High Knees?
- Stand tall and rapidly drive knees up toward chest while pumping arms
- Aim to bring knees to hip level or higher, landing on balls of feet
- Maintain upright posture and continue rapid alternating motion throughout interval
5. Push-up to T
Push-up to T combines upper body strength training with core rotation, creating a comprehensive exercise that challenges multiple muscle groups while maintaining elevated heart rate. This movement targets chest, shoulders, triceps, and core while improving stability and coordination through rotational components. The combination of pushing and rotating makes this exercise excellent for building functional strength during HIIT workouts.
How to Do Push-up to T?
- Perform standard push-up, then rotate into side plank with one arm reaching toward ceiling
- Hold T position briefly, return to plank, then push-up and rotate to opposite side
- Alternate rotation directions with each repetition, maintaining controlled movement throughout
6. Plank Jacks
Plank jacks combine isometric core training with dynamic leg movements, creating intense abdominal and shoulder challenges while maintaining cardiovascular demand. This exercise builds core stability and shoulder endurance while providing excellent calorie burn through sustained muscle engagement. The combination of static and dynamic elements makes plank jacks perfect for HIIT training while developing functional core strength.
How to Do Plank Jacks?
- Start in plank position with feet together, maintaining straight body line
- Jump feet apart and back together while keeping hands planted and core engaged
- Maintain stable upper body throughout movement, avoiding hip bouncing or sagging
7. Jumping Lunges
Jumping lunges combine unilateral leg training with explosive plyometric power, creating intense lower body conditioning while challenging balance and coordination. This exercise develops single-leg strength and power while providing exceptional calorie burn through continuous explosive movements. The alternating leg pattern makes jumping lunges excellent for building athletic performance while maximizing HIIT training effectiveness.
How to Do Jumping Lunges?
- Start in lunge position, then explosively jump up while switching leg positions mid-air
- Land softly in opposite lunge position with control and proper knee alignment
- Immediately jump into next repetition, maintaining rapid alternating pattern throughout
8. Bear Crawl
Bear crawl challenges the entire body through quadrupedal movement patterns while providing intense core and shoulder training during HIIT sessions. This exercise improves shoulder stability, core strength, and coordination while maintaining elevated heart rate for maximum calorie burn. The primal movement pattern engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously while building functional strength and movement quality.
How to Do Bear Crawl?
- Start on hands and knees, lift knees slightly off ground maintaining low position
- Move forward by advancing opposite hand and foot simultaneously in crawling pattern
- Keep back flat and hips level while taking small controlled steps throughout movement
9. Tuck Jumps
Tuck jumps develop explosive lower body power while providing intense cardiovascular conditioning through maximum effort jumping movements. This advanced plyometric exercise builds fast-twitch muscle fibers while delivering exceptional calorie burn during high-intensity intervals. The explosive nature challenges multiple energy systems while developing athletic power and coordination essential for sports performance.
How to Do Tuck Jumps?
- Start standing with feet hip-width apart, arms at sides for momentum
- Jump up explosively while bringing knees toward chest in tucked position
- Land softly with bent knees and immediately prepare for next explosive jump
10. Russian Twists
Russian twists target the core muscles and obliques while providing moderate cardiovascular challenge during HIIT recovery periods or active rest. This exercise builds rotational core strength while maintaining movement and calorie burn between higher intensity exercises. The twisting motion develops functional core stability while serving as an excellent transition exercise during circuit training.
How to Do Russian Twists?
- Sit with knees bent and lean back slightly, lifting feet off ground if possible
- Rotate torso side to side while keeping chest up and core engaged
- Move with control rather than speed, focusing on core muscle activation throughout
Learn exactly how many calories to burn to lose 1 kg.
Factors That Affect How Many Calories You Burn in HIIT
Understanding the variables that influence calorie burn helps optimize your HIIT sessions for maximum effectiveness. Your body composition, fitness level, and workout structure all play significant roles in determining energy expenditure during exercise sessions.
Body weight remains the primary factor affecting how many calories do you burn in hiit workouts. Heavier individuals require more energy to move their body mass during exercises, resulting in higher calorie burn rates. Additionally, muscle mass influences calorie burn since muscle tissue is metabolically active and requires more energy to function than fat tissue during exercise.
Workout intensity directly impacts calorie expenditure, with higher intensities producing greater energy demands. The specific exercises chosen also matter significantly – full-body movements like burpees, mountain climbers, and jumping jacks burn more calories than isolated exercises. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can also affect calorie burn rates.
Mountain climbers calorie burn: how many calories burned in mountain climbers
Exercise Selection Impact
Choosing the right exercises maximizes calorie burn during your 45-minute HIIT sessions. Compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously create the highest energy demands and calorie expenditure rates. Full-body exercises like burpees combine cardiovascular and strength training elements, making them extremely effective for burning calories. Similarly, plyometric movements such as jump squats and box jumps require explosive power that significantly increases energy expenditure compared to static exercises.
See results from box jumps calories burned.
Individual Fitness Level
Your current fitness condition affects both immediate calorie burn and long-term adaptation to HIIT training. Beginners often burn fewer calories initially due to lower work capacity, but they also experience rapid improvements in calorie-burning efficiency as fitness improves.
More experienced athletes can maintain higher intensities throughout entire sessions, resulting in greater total calorie expenditure. However, their bodies also become more efficient at performing exercises, potentially reducing calorie burn per minute compared to when they first started training.
Combine training with nutrition: intermittent fasting plan that supports fat loss and muscle retention.

How Many Times HIIT Per Week for Optimal Results?
Determining the right frequency for HIIT workouts balances effectiveness with recovery needs. Most fitness experts recommend 2-3 HIIT sessions per week for optimal results without overtraining. This frequency allows adequate recovery time between intense sessions while maintaining consistent calorie burn and fitness improvements. When considering how many times hiit per week to perform, beginners should start with 1-2 sessions weekly and gradually increase frequency as fitness improves. Advanced practitioners can handle 3-4 sessions per week, but should include variety in exercise selection and intensity levels to prevent plateaus and overuse injuries.
- Beginners: Start with 1-2 HIIT sessions per week
- Intermediate: Progress to 2-3 sessions weekly with 24-48 hours rest between workouts
- Advanced: Can handle 3-4 sessions per week with proper program variation
- Recovery Focus: Always include at least one full rest day between intense HIIT sessions
- Listen to Body: Reduce frequency if experiencing excessive fatigue or soreness
- Cross-Training: Combine HIIT with other exercise types for balanced fitness development
The timing of your HIIT sessions throughout the week also matters for recovery and performance. Spacing sessions evenly allows better recovery, such as performing HIIT on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday with rest or light activity days between.
Find out how much calories do leg raises burn for abs training.
How Many Calories Does a HIIT Workout Burn by Duration?
Workout duration significantly influences total calorie expenditure, with longer sessions generally burning more calories. However, the relationship isn’t perfectly linear due to fatigue effects and decreased intensity as workouts progress beyond optimal durations.
Understanding how many calories does a hiit workout burn across different time periods helps you choose appropriate session lengths based on your goals, fitness level, and available time. Shorter, more intense sessions can be highly effective, while longer sessions may require reduced intensity to maintain quality throughout.
| Duration | Calories Burned | Intensity Level | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 minutes | 150-250 calories | Very High | Beginners, Time-Crunched |
| 20 minutes | 200-350 calories | High | Most People |
| 30 minutes | 250-450 calories | Moderate-High | Intermediate |
| 45 minutes | 375-600 calories | Moderate | Advanced |
| 60 minutes | 450-750 calories | Moderate | Very Advanced |
Shorter HIIT sessions typically allow for higher intensity levels throughout the entire workout, potentially resulting in greater calorie burn per minute. However, longer sessions provide more total calorie expenditure and may better support endurance adaptations alongside strength and power improvements.
The sweet spot for most people lies between 20-30 minutes of HIIT, providing substantial calorie burn while maintaining high intensity levels throughout the session. This duration also fits well into busy schedules and reduces the risk of overtraining when performed multiple times per week.
30-Minute HIIT Calorie Burn
A 30-minute HIIT session represents the most popular workout duration, balancing effectiveness with practicality. Most people can maintain high intensity levels throughout this timeframe while achieving significant calorie burn and fitness benefits.
How many calories burned in 30 min hiit typically ranges from 250-450 calories depending on body weight and intensity. This duration allows for proper warm-up, multiple work-rest cycles, and adequate cool-down while fitting into most daily schedules effectively.
Hour-Long HIIT Sessions
Extended HIIT sessions of 60 minutes can burn substantial calories but require careful programming to maintain effectiveness. The question of 1 hour of hiit burns how many calories typically yields answers between 450-750 calories for most individuals.
However, maintaining true HIIT intensity for a full hour is extremely challenging and may not be sustainable for most people. Longer sessions often incorporate more rest periods or reduced intensity to prevent premature fatigue and maintain movement quality throughout the workout.
Explore the best compound dumbbell exercises for muscle and fat loss.

HIIT Workout Frequency for Different Goals
Your training goals should determine how many days should you do hiit and the specific structure of your weekly exercise routine. Weight loss goals may benefit from different frequency recommendations compared to athletic performance or general fitness objectives.
For fat loss and weight management, performing HIIT 3-4 times per week combined with proper nutrition creates significant calorie deficits. The afterburn effect from HIIT sessions continues burning calories for hours after workouts, making this frequency particularly effective for body composition changes.
Athletes training for specific sports may use HIIT less frequently, perhaps 1-2 times per week, focusing on sport-specific energy system development rather than maximum calorie burn. General fitness enthusiasts typically achieve best results with 2-3 HIIT sessions weekly combined with other exercise types.
Weight Loss Focus
When weight loss is the primary goal, hiit how many times a week becomes crucial for creating consistent calorie deficits. Three HIIT sessions per week, combined with 2-3 strength training sessions, provides excellent results for most people attempting to lose body fat.
This frequency creates substantial weekly calorie expenditure while allowing adequate recovery between intense sessions. The combination of immediate calorie burn during workouts plus extended afterburn effects helps create the energy deficit necessary for sustainable weight loss over time.
Athletic Performance
Athletes use HIIT strategically to improve specific energy systems relevant to their sport. The frequency question of hiit workout how many times a week for athletes depends on their sport’s demands, training phase, and other workout commitments.
Endurance athletes might use HIIT once weekly during base training phases but increase frequency during specific preparation periods. Power athletes may incorporate HIIT 2-3 times weekly year-round to maintain cardiovascular fitness alongside strength and power development.

Maximizing Calorie Burn During HIIT Sessions
Optimizing your HIIT workouts involves strategic exercise selection, proper intensity management, and smart programming decisions. Understanding these factors helps you get the most calorie burn from every session while maintaining safety and sustainability.
Exercise selection dramatically impacts calorie expenditure, with compound movements burning significantly more energy than isolation exercises. Combining upper body, lower body, and core exercises in circuit formats creates maximum metabolic demand and calorie burn throughout your workout sessions.
Proper work-to-rest ratios ensure you can maintain high intensity throughout your session. Common ratios include 1:1 (30 seconds work, 30 seconds rest), 2:1 (40 seconds work, 20 seconds rest), and 1:2 (20 seconds work, 40 seconds rest) depending on your fitness level and goals.
High-Calorie Burning Exercises
Certain exercises consistently produce higher calorie burn rates due to their movement complexity and muscle recruitment patterns. Incorporating these exercises into your HIIT routines maximizes energy expenditure and workout effectiveness.
Burpees consistently rank as one of the highest calorie-burning exercises, combining squat, plank, push-up, and jump movements into one fluid exercise. Mountain climbers provide similar benefits while being more accessible for beginners who may struggle with full burpees initially.
Discover more about jumping jacks exercise benefits and how they complement HIIT routines perfectly.
Programming Strategies
Effective HIIT programming balances intensity, duration, and recovery to maximize calorie burn while preventing overtraining. Progressive overload principles apply to HIIT just like strength training, requiring gradual increases in difficulty over time.
Varying workout formats prevents adaptation and keeps calorie burn high as your fitness improves. Alternating between different interval lengths, exercise selections, and intensity levels challenges your body in new ways and maintains high energy expenditure rates.
Learn how to do jumping jacks properly to maximize their calorie-burning potential in your HIIT workouts.
Creating Effective HIIT Routines for Maximum Calorie Burn
Designing HIIT workouts that maximize calorie burn requires understanding exercise progression, intensity management, and recovery integration. Well-structured routines balance effectiveness with sustainability, ensuring you can maintain high performance across multiple weekly sessions.
Workout structure typically includes a 5-10 minute warm-up, 15-30 minutes of interval training, and 5-10 minutes of cool-down. This framework allows proper preparation, maximum effort during work intervals, and adequate recovery to prevent injury and support adaptation.
Exercise selection should emphasize compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Combining cardiovascular challenges with strength elements creates the highest calorie burn rates while improving overall fitness capacity and functional strength.
- Warm-up Phase: 5-10 minutes of gradually increasing intensity
- Work Intervals: 15-60 seconds at 80-95% maximum effort
- Rest Intervals: 15-90 seconds of low-intensity recovery or complete rest
- Exercise Variety: Include upper body, lower body, and full-body movements
- Cool-down: 5-10 minutes of decreasing intensity and stretching
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase intensity, duration, or complexity over time
The key to sustainable HIIT programming lies in balancing challenge with recovery. Each workout should feel demanding but not completely exhausting, allowing you to maintain quality movement patterns and high intensity throughout the session.
Beginner HIIT Structure
New to HIIT training should start with simpler movement patterns and longer recovery periods to build fitness gradually. Beginning with bodyweight exercises reduces injury risk while allowing focus on proper form and intensity management.
A typical beginner session might include 20 seconds of work followed by 40 seconds of rest, repeated for 10-15 minutes total. This structure provides adequate recovery while still challenging the cardiovascular system and burning significant calories for newcomers to intense exercise.
Explore calisthenics equipment for home to enhance your HIIT workouts with minimal equipment needs.
Advanced HIIT Programming
Experienced exercisers can handle more complex movements, shorter rest periods, and longer overall session durations. Advanced programming might include equipment like kettlebells, medicine balls, or bodyweight variations that increase difficulty significantly.
Work-to-rest ratios can progress to 1:1 or even 2:1 as fitness improves, allowing greater total work volume and calorie burn. Advanced sessions might last 30-45 minutes with multiple blocks of different exercise types and intensity levels.
Recovery and HIIT Frequency Guidelines
Proper recovery between HIIT sessions is essential for maintaining high performance and preventing overtraining symptoms. The intense nature of these workouts creates significant stress on multiple body systems, requiring adequate time for repair and adaptation.
Signs of insufficient recovery include decreased performance, excessive fatigue, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and increased susceptibility to illness. Recognizing these symptoms early allows you to adjust training frequency before serious overtraining develops.
Active recovery days between HIIT sessions can include light walking, gentle yoga, or mobility work. These activities promote blood flow and recovery without adding significant stress to already challenged systems. Complete rest days are also important, especially for beginners or during periods of high life stress.
Recovery Strategies
Implementing effective recovery strategies between HIIT sessions supports better performance and higher calorie burn in subsequent workouts. Proper nutrition, hydration, and sleep form the foundation of good recovery practices.
Post-workout nutrition should include both carbohydrates to replenish energy stores and protein to support muscle recovery. Consuming these nutrients within 30-60 minutes after exercise optimizes the recovery process and prepares your body for the next training session.
Check out how to do glute bridge exercises that can serve as excellent recovery and activation movements between intense HIIT sessions.
Managing Training Load
Balancing HIIT frequency with other exercise types prevents overuse injuries and maintains high performance levels. Combining HIIT with strength training, flexibility work, and low-intensity cardio creates well-rounded fitness development.
Monitoring your response to training helps determine optimal frequency and intensity levels. Keeping track of performance metrics, energy levels, and recovery indicators guides programming decisions and prevents excessive training stress.
Learn about resistance band exercises for abs that complement HIIT training for complete core development.

Nutrition and HIIT Performance
Proper nutrition significantly impacts both HIIT performance and recovery, influencing how many calories you burn during workouts and how quickly you recover between sessions. Pre-workout fueling affects your ability to maintain high intensity throughout the session, while post-workout nutrition supports recovery and adaptation.
Carbohydrate availability influences high-intensity performance more than other macronutrients. Having adequate glycogen stores allows you to maintain power output during work intervals, maximizing calorie burn throughout the session. However, exercising in a slightly fasted state may enhance fat oxidation during recovery periods.
Hydration status dramatically affects exercise performance and calorie burn efficiency. Even mild dehydration can reduce exercise capacity and limit your ability to maintain high intensities during HIIT sessions. Proper hydration before, during, and after workouts supports optimal performance.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Timing and composition of pre-workout meals influence HIIT performance and calorie burn potential. Eating 1-3 hours before exercise provides energy without causing digestive discomfort during intense intervals.
Light snacks 30-60 minutes before training can provide quick energy for high-intensity efforts. Options like bananas, dates, or small amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates help maintain blood sugar levels during demanding workouts.
Post-Workout Recovery Nutrition
Post-exercise nutrition supports recovery processes and prepares your body for subsequent training sessions. Consuming protein and carbohydrates within the post-workout window helps optimize recovery and maintain consistent performance.
The combination of nutrients helps replenish energy stores while supporting muscle protein synthesis. This recovery nutrition becomes increasingly important as training frequency increases and workout intensity remains high.
Explore arm workouts with dumbbells women’s programs that can complement your HIIT routine for complete upper body development.
Tracking HIIT Calorie Burn Progress
Monitoring your calorie burn and fitness progress helps optimize HIIT programming and maintain motivation for consistent training. Various methods exist for tracking energy expenditure, each with different accuracy levels and practical considerations.
Heart rate monitors provide relatively accurate calorie burn estimates during HIIT sessions by tracking intensity levels throughout workouts. These devices account for individual differences in fitness level and effort, providing personalized calorie expenditure data for each session.
Fitness trackers and smartphone apps offer convenient tracking options, though accuracy may vary significantly between devices and individuals. Using multiple tracking methods and focusing on trends rather than absolute numbers provides the best insight into your progress over time.
Performance Metrics
Beyond calorie burn, tracking performance metrics helps ensure your HIIT program continues delivering results. Monitoring work capacity, recovery heart rate, and exercise progression provides valuable feedback about fitness improvements and program effectiveness.
Keeping workout logs that include exercises performed, intensities achieved, and subjective energy levels helps identify patterns and optimize your training approach. This data becomes particularly valuable for adjusting frequency and intensity based on your body’s responses.
Technology Tools
Modern technology offers numerous options for tracking HIIT workouts and calorie burn. Wearable devices, smartphone applications, and gym equipment with built-in monitoring provide different approaches to workout tracking and progress monitoring.
Choosing tracking methods that you’ll use consistently matters more than finding the most accurate device. Simple logging methods often provide better long-term adherence than complex tracking systems that become burdensome over time.
Learn how to do arnold press to add effective shoulder training to your fitness routine alongside HIIT workouts.

Common HIIT Mistakes That Reduce Calorie Burn
Several common errors reduce the effectiveness of HIIT workouts and limit calorie burn potential. Understanding these mistakes helps you optimize your training approach and achieve better results from your exercise time investment.
Insufficient intensity during work intervals represents the most common HIIT mistake. Many people exercise at moderate intensity throughout entire sessions rather than truly high-intensity intervals followed by adequate recovery periods. This approach reduces both immediate calorie burn and afterburn effects.
Inadequate recovery between intervals prevents you from maintaining high intensities during subsequent work periods. Taking too little rest leads to decreasing performance throughout the session, ultimately reducing total calorie expenditure and training effectiveness.
- Low Work Intensity: Failing to reach 80-90% maximum effort during work intervals
- Insufficient Recovery: Not allowing adequate rest between high-intensity intervals
- Poor Exercise Selection: Choosing exercises that don’t challenge multiple muscle groups
- Excessive Frequency: Training too often without adequate recovery time
- Ignoring Form: Sacrificing movement quality for speed or intensity
- Inconsistent Timing: Varying interval lengths without strategic purpose
- Inadequate Warm-up: Starting high-intensity work without proper preparation
Avoiding these mistakes requires honest assessment of your effort levels and commitment to proper workout structure. Using heart rate monitoring or perceived exertion scales helps ensure you’re working at appropriate intensities during each phase of your HIIT sessions.
Form and Technique
Maintaining proper exercise form becomes challenging during high-intensity intervals, but poor technique reduces effectiveness and increases injury risk. Focusing on movement quality rather than just speed ensures maximum muscle recruitment and calorie burn.
Complex exercises require extra attention to form during HIIT sessions. Starting with simpler movement patterns and progressing to more challenging exercises as technique improves helps maintain safety while maximizing calorie burn over time.
Discover how to do plank exercise correctly to build core strength that supports proper form during intense HIIT movements.
Programming Errors
Poor program design limits HIIT effectiveness regardless of effort level during individual sessions. Understanding proper work-to-rest ratios, exercise selection, and progression principles ensures your program continues delivering results over time.
Random workout selection without progressive structure often leads to plateaus in both performance and calorie burn. Following systematic progression plans maintains challenge levels and supports continued improvement in fitness and body composition.
Advanced HIIT Strategies for Maximum Calorie Burn
Experienced HIIT practitioners can implement advanced strategies to further increase calorie burn and training effectiveness. These techniques require solid fitness base and proper understanding of training principles before implementation.
Density training increases workout volume by gradually reducing rest periods between intervals while maintaining exercise intensity. This approach increases total work performed per session, resulting in higher calorie burn and improved work capacity over time.
Combining different training modalities within single sessions can enhance calorie burn. Integrating strength exercises with cardiovascular intervals challenges different energy systems simultaneously, creating greater metabolic demand and calorie expenditure.
Complex Training Methods
Advanced HIIT methods combine different exercise types and intensities to create maximum metabolic challenge. These approaches require careful programming to balance effectiveness with recovery needs.
Contrast training alternates between power exercises and strength exercises within single sessions. This approach challenges different muscle fiber types and energy systems, creating comprehensive training stimulus and elevated calorie burn rates.
Periodization Strategies
Systematic variation in HIIT programming prevents adaptation and maintains high calorie burn rates as fitness improves. Periodization involves planned changes in intensity, volume, and exercise selection over time.
Linear periodization gradually increases training challenge over several weeks or months. Undulating periodization varies training stress within shorter timeframes, keeping the body challenged and maintaining high energy expenditure rates.
Check out chest and tricep workout with dumbbells routines that can be incorporated into advanced HIIT programming for comprehensive upper body training.
HIIT Safety Considerations and Injury Prevention
High-intensity training carries inherent injury risks that require proper management and prevention strategies. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safety measures ensures you can maintain consistent training and maximize long-term calorie burn benefits.
Proper warm-up becomes critically important before HIIT sessions due to the immediate high-intensity demands. Spending adequate time preparing your cardiovascular system, muscles, and joints for intense exercise reduces injury risk and improves performance during work intervals.
Movement quality should never be sacrificed for intensity or speed during HIIT workouts. Maintaining proper form throughout all exercises protects joints and ensures maximum muscle recruitment, leading to better results and fewer injuries over time.
Injury Prevention Protocols
Implementing systematic injury prevention strategies protects your ability to train consistently and maintain high calorie burn rates. These protocols become increasingly important as training frequency and intensity increase.
Progressive overload principles apply to HIIT training just like strength training. Gradually increasing challenge levels allows your body to adapt safely while continuing to provide effective training stimulus and calorie burn benefits.
Medical Considerations
Certain medical conditions require modified approaches to HIIT training or medical clearance before beginning intense exercise programs. Understanding contraindications and risk factors helps ensure safe participation in high-intensity training.
Individuals with cardiovascular conditions, joint problems, or metabolic disorders should consult healthcare providers before beginning HIIT programs. Modified versions of HIIT can often provide similar benefits with reduced risk for people with medical considerations.
Learn about bodybuilding exercises at home that can serve as lower-intensity alternatives or complementary training to HIIT workouts.
Conclusion
Understanding how many calories does 45 minutes of HIIT burn empowers you to make informed decisions about your fitness routine and weight management goals. The 375-600 calorie burn range for most people makes HIIT an efficient exercise choice for busy schedules. Remember that consistency in training frequency, proper form, and adequate recovery between sessions determine long-term success more than any single workout’s calorie burn.
The effectiveness of HIIT extends beyond immediate calorie burn through the afterburn effect, making it particularly valuable for weight loss and body composition improvement. Combined with proper nutrition and realistic frequency guidelines of 2-3 sessions per week, HIIT can be a powerful tool in achieving your fitness goals while fitting into demanding daily schedules.
Explore calisthenics chest exercises to add variety to your HIIT routines with bodyweight movements that require no equipment but deliver excellent results.
Want to master the calisthenics handstand and take your skills to the next level? Whether you’re a beginner or pushing advanced skills, ISC – Indian School of Calisthenics offers expert guidance to help you master bodyweight training. Visit us at SRPF Ground, NH8, Goregaon (E), Mumbai – 400065. For class schedules, personalized coaching, or more details, call +91 77159 53218. Train smart, move better, and unlock your back strength with ISC
How Many Calories Does 45 Minutes of HIIT Burn? – FAQs
How many calories does 45 minutes of HIIT burn for beginners?
Beginners typically burn 300-450 calories in 45 minutes of HIIT, depending on body weight and intensity level achieved.
Can I do HIIT workouts every day for maximum calorie burn?
No, HIIT should be limited to 2-3 times per week to allow proper recovery and prevent overtraining.
How does body weight affect how many calories does 45 minutes of HIIT burn?
Heavier individuals burn more calories, with approximately 50-75 additional calories per 10 kg of body weight.
What’s the difference in calorie burn between 30 and 45-minute HIIT sessions?
A 45-minute session typically burns 125-150 more calories than a 30-minute session of similar intensity.
How many calories do you burn in HIIT compared to steady-state cardio?
HIIT burns 25-30% more calories per minute than steady-state cardio of the same duration.
Does the afterburn effect significantly increase total calories burned from HIIT?
Yes, EPOC can increase total daily calorie burn by an additional 50-150 calories after intense HIIT sessions.
How many times HIIT per week is optimal for weight loss?
Three HIIT sessions per week, combined with proper nutrition, provides optimal results for most weight loss goals.
What factors affect how many calories does a HIIT workout burn?
Body weight, intensity level, exercise selection, fitness level, and workout duration all significantly impact calorie burn.
How many days should you do HIIT to avoid overtraining?
Most people should limit HIIT to 3 days per week maximum, with rest days between sessions.
Can 1 hour of HIIT burns how many calories for advanced athletes?
Advanced athletes can burn 600-900 calories in one hour of high-intensity HIIT training, depending on their size and effort level.