How to do reverse lunges correctly involves stepping one foot backward, lowering both knees to 90 degrees, and pushing through the front heel to return to starting position.
Learning how to do reverse lunges correctly opens doors to one of the most effective lower body exercises for building strength and stability. This powerful movement targets your glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and core while being gentler on your knees than forward lunges. Many fitness enthusiasts prefer reverse lunges because they offer better control and reduced joint stress.
The beauty of understanding how to do reverse lunges correctly lies in their versatility and accessibility. Whether you’re a beginner starting your fitness journey or an advanced athlete looking to improve performance, mastering proper reverse lunge technique provides a foundation for functional movement. This exercise mimics everyday activities like stepping down stairs or getting up from a kneeling position. When you learn how to do reverse lunges correctly, you’ll discover why physical therapists and trainers recommend this movement for people with knee concerns. The backward stepping motion keeps your front knee in a safer position, reducing stress on the joint while maximizing muscle activation. This makes reverse lunges an excellent choice for building lower body strength without compromising joint health.
Table of Contents
How to Do Reverse Lunges Correctly Step-by-Step?
Understanding how to do reverse lunges correctly requires mastering each phase of the movement with precision and control. This fundamental exercise demands proper body alignment, controlled movement patterns, and consistent technique to maximize benefits while minimizing injury risk. Breaking down the movement into manageable steps helps build confidence and competence. The key to learning how to do reverse lunges correctly starts with establishing a stable foundation and maintaining proper posture throughout the entire range of motion. Each component of the movement serves a specific purpose in developing strength, balance, and coordination.
| Step | Action | Key Focus | Common Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Starting Position | Feet hip-width apart, upright posture | Too narrow or wide stance |
| 2 | Step Backward | Step back 2-3 feet, toe first contact | Step too short or long |
| 3 | Descend | Lower both knees to 90 degrees | Front knee drifting forward |
| 4 | Bottom Position | Both legs at 90-degree angles | Leaning forward too much |
| 5 | Ascent | Push through front heel to rise | Using back leg to push off |
| 6 | Return | Bring back foot to starting position | Rushing the movement |
Step 1: Establishing Starting Position
Creating a stable foundation when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly begins with proper foot placement and body alignment. Stand tall with feet positioned hip-width apart, ensuring even weight distribution across both feet. Keep your shoulders back, chest up, and core muscles engaged to maintain spinal neutrality throughout the movement preparation phase.
- Keep feet parallel and hip-width apart for optimal balance
- Engage core muscles before initiating any movement
- Maintain neutral head position looking straight ahead
- Distribute weight evenly across both feet initially
Step 2: Stepping Backward Technique
The backward step phase of how to do reverse lunges correctly requires controlled movement and proper distance judgment. Step directly backward with one foot, landing on the ball of the foot first. The step distance should be approximately 2-3 feet or far enough to allow both knees to reach 90-degree angles comfortably at the bottom position.
- Step straight back, not at an angle
- Land on ball of back foot, not the heel
- Maintain hip-width stance throughout the step
- Control the stepping speed to maintain balance
Step 3: Controlled Descent Phase
Lowering your body when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly involves simultaneous bending of both knees while maintaining an upright torso. Focus on keeping most of your weight on the front leg while using the back leg primarily for balance and support. Descend until both knees reach approximately 90-degree angles.
- Keep 80% of weight on the front leg
- Lower straight down, not forward or backward
- Maintain upright torso throughout descent
- Stop when back knee nearly touches the floor
Step 4: Bottom Position Hold
The bottom position of how to do reverse lunges correctly represents the point of maximum muscle activation and stretch. Both legs should form 90-degree angles with the front thigh parallel to the floor and back knee hovering just above the ground. Maintain this position briefly to maximize muscle engagement before beginning the ascent phase.
- Check that front knee stays over ankle, not forward
- Keep back knee pointing straight down toward floor
- Maintain upright posture without leaning forward
- Feel stretch in back leg hip flexor muscles
Step 5: Powerful Ascent Movement
Rising from the bottom position when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly requires driving forcefully through the front heel. Focus on pushing the ground away with the front foot while keeping the torso upright. The movement should be controlled but powerful, engaging the glutes and quadriceps of the front leg to return to the starting position.
- Drive primarily through the front heel, not toes
- Keep front knee aligned over ankle during ascent
- Squeeze glutes at the top of the movement
- Maintain controlled speed throughout the rise
Step 6: Return to Starting Position
Completing the movement when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly involves bringing the back foot forward to return to the starting position. Step forward with control, avoiding any bouncing or rushing motions. Reset your stance and prepare for the next repetition or switch to the opposite leg depending on your training protocol.
- Control the forward step back to start position
- Reset stance width to hip-width apart
- Pause briefly between repetitions for form check
- Alternate legs or complete all reps on one side first
Learn arm workouts with dumbbells women’s and how to do plank exercise for complete fitness.
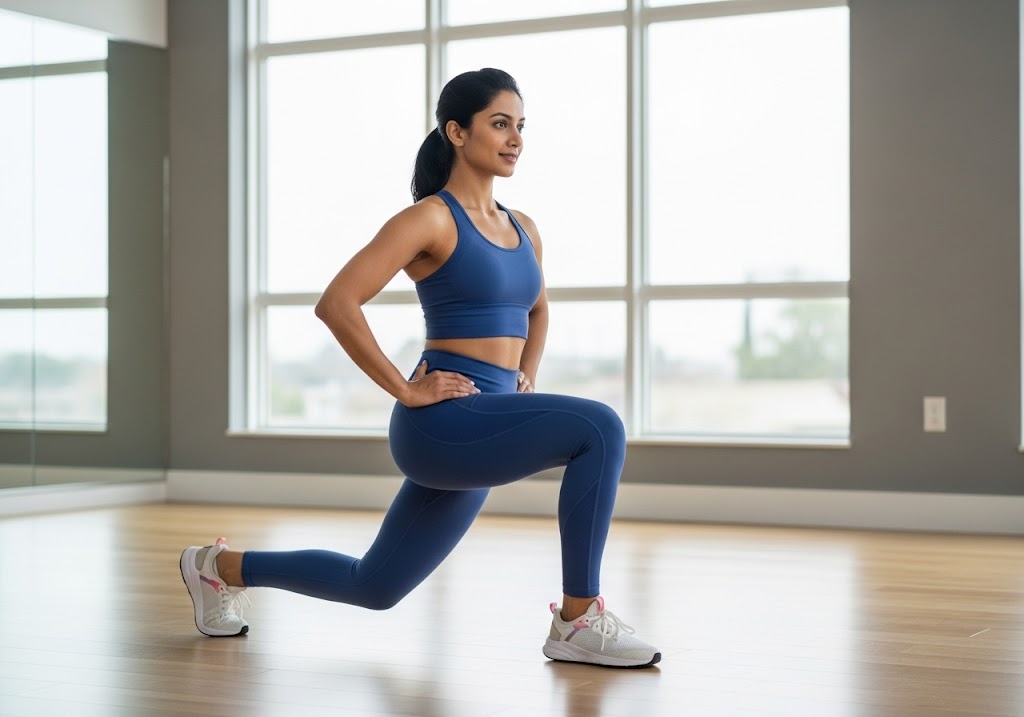

Reverse Lunge Benefits
Learning how to do reverse lunges correctly provides numerous advantages that extend beyond simple leg strengthening. These benefits include improved functional movement patterns, enhanced balance and stability, and reduced joint stress compared to forward lunging variations. Understanding these advantages motivates consistent practice and proper technique development.
The comprehensive benefits of knowing how to do reverse lunges correctly make this exercise valuable for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone seeking to improve lower body strength and function.
- Knee-Friendly Design – Stepping backward keeps front knee behind toes, reducing harmful shear forces on the joint
- Enhanced Glute Activation – Emphasizes posterior chain muscles more than forward lunges for better hip strength and stability
- Improved Balance and Coordination – Single-leg stance challenges proprioception and develops functional stability skills
- Unilateral Strength Development – Works each leg independently to address muscle imbalances and weakness patterns
- Core Stabilization – Requires deep core engagement to maintain upright posture throughout the movement
- Functional Movement Pattern – Mimics everyday activities like stepping down stairs or rising from kneeling positions
- Versatile Loading Options – Can be performed with bodyweight or various equipment for progressive overload
- Reduced Fall Risk – Builds single-leg strength and balance that translates to better daily movement confidence
- Athletic Performance Enhancement – Develops unilateral power and stability crucial for sports performance
- Rehabilitation Friendly – Often prescribed by physical therapists for knee and hip injury recovery
Discover resistance band exercises for abs and understand does calisthenics increase height.
Reverse Lunges Muscles Worked
Understanding which muscles are engaged when you learn how to do reverse lunges correctly helps optimize your training approach and ensures balanced development. This exercise activates multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it highly efficient for building functional strength and muscle mass throughout the lower body.
The muscle activation pattern when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly demonstrates why this exercise ranks among the most effective compound movements for lower body development.
| Muscle Group | Primary/Secondary | Function | Activation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutes (Gluteus Maximus) | Primary | Hip extension, stabilization | High |
| Quadriceps | Primary | Knee extension, body control | High |
| Hamstrings | Primary | Hip extension, knee stabilization | Medium-High |
| Calves (Gastrocnemius/Soleus) | Secondary | Ankle stabilization, push-off | Medium |
| Core Muscles | Secondary | Torso stabilization, balance | Medium |
| Hip Adductors | Secondary | Hip stabilization, alignment | Low-Medium |
Learn more about how to do a perfect squat to complement your reverse lunge training.
Primary Muscle Groups
The primary muscle groups activated when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly include the glutes, quadriceps, and hamstrings, which work together to generate force and control movement throughout the exercise.
Secondary Stabilizing Muscles
Secondary muscles engaged during how to do reverse lunges correctly provide crucial stabilization and support, including the core muscles, calves, and hip adductors that maintain proper alignment and balance.

Reverse Lunge vs Forward Lunge
Comparing reverse lunges to forward lunges reveals significant differences in muscle emphasis, joint stress, and movement difficulty when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly. Understanding these distinctions helps choose the most appropriate variation for your goals and physical limitations.
| Aspect | Reverse Lunge | Forward Lunge | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knee Safety | Lower stress, knee stays behind toes | Higher stress, knee may drift forward | Reverse Lunge |
| Muscle Emphasis | Glutes and hamstrings dominant | Quadriceps dominant | Depends on goals |
| Balance Challenge | More stable, easier to control | Less stable, requires more balance | Forward Lunge |
| Beginner Friendly | Easier to learn and master | More challenging coordination | Reverse Lunge |
| Core Activation | Moderate core engagement | Higher core activation needed | Forward Lunge |
| Functional Movement | Mimics stepping down stairs | Mimics walking forward | Tie |
| Joint Mobility Required | Moderate flexibility needs | Higher ankle/hip mobility needs | Reverse Lunge |
| Loading Potential | Easier to add heavy weights | Harder to load safely | Reverse Lunge |
| Athletic Performance | Good for stability training | Better for deceleration training | Depends on sport |
| Injury Risk | Lower risk with proper form | Higher risk if form breaks down | Reverse Lunge |
Both exercises target similar muscle groups but with varying degrees of activation and safety considerations. Each direction offers unique benefits and challenges that serve different training purposes.
Discover calisthenics for weight loss to incorporate reverse lunges into a comprehensive fat-burning routine.
How to Do Reverse Lunges Correctly with Dumbbells?
Adding dumbbells when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly increases resistance and challenges your muscles more intensively while developing functional strength patterns. Proper dumbbell positioning and weight selection ensure safe and effective strength development progression.
| Dumbbell Position | Difficulty Level | Muscle Emphasis | Stability Challenge | Weight Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arms at Sides | Beginner-Intermediate | Legs and Glutes | Low-Moderate | 5-15 kg per dumbbell |
| Shoulder Level | Intermediate | Legs, Core, Shoulders | Moderate-High | 8-20 kg per dumbbell |
| Goblet Hold | Beginner-Intermediate | Core, Legs | Moderate | 8-25 kg single dumbbell |
| Overhead Hold | Advanced | Full Body | Very High | 5-15 kg per dumbbell |
| Single Arm | Intermediate-Advanced | Core, Anti-rotation | High | 8-20 kg single dumbbell |
| Farmer’s Carry Style | Intermediate | Grip, Traps, Legs | Low-Moderate | 10-30 kg per dumbbell |
Step 1: Dumbbell Selection and Grip
Choosing appropriate dumbbell weights when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly with added resistance requires starting conservatively and progressing gradually. Select weights that allow perfect form maintenance throughout all repetitions while still providing muscular challenge. Begin with lighter weights to master the coordination between lunging movement and weight control before advancing to heavier loads.
- Start with 50-70% of your bodyweight squat weight
- Test grip security before beginning the exercise
- Choose weights that don’t compromise your balance
- Have a spotter available when using heavy weights
Step 2: Starting Position with Dumbbells
Establishing proper starting position while holding dumbbells when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly requires extra attention to posture and core engagement. Stand with feet hip-width apart while holding dumbbells in your chosen position. Maintain upright torso alignment and engage core muscles more intensely to support the additional weight load throughout the movement.
- Engage core muscles before lifting dumbbells
- Keep shoulders back and down throughout exercise
- Maintain neutral spine alignment with added weight
- Check that grip remains secure before starting
Step 3: Weighted Backward Step
Stepping backward while holding dumbbells when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly demands greater balance and coordination than bodyweight versions. Control the backward step carefully, ensuring the added weight doesn’t pull you off balance. Step the same distance as bodyweight lunges while maintaining the dumbbell position throughout the stepping motion and descent phase.
- Step at same pace as bodyweight version
- Don’t let weights pull you forward or backward
- Maintain chosen dumbbell position throughout step
- Keep core engaged to resist weight displacement
Step 4: Controlled Descent with Resistance
Lowering into the lunge position while holding dumbbells requires enhanced muscle control and coordination when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly with added resistance. The additional weight increases the challenge on your legs and core while potentially affecting your balance. Focus on maintaining the same movement pattern as bodyweight lunges despite the increased loading.
- Descend at slightly slower pace than bodyweight
- Keep dumbbells in stable position throughout descent
- Don’t allow weights to swing or shift position
- Maintain same depth as bodyweight version
Step 5: Weighted Bottom Position
Holding the bottom position while managing dumbbell weight when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly with resistance requires enhanced stability and strength. The added load increases muscle activation throughout your lower body while challenging your core stability. Brief pause at bottom position ensures maximum benefit from the increased resistance before beginning the ascent phase.
- Hold position for 1-2 seconds with control
- Check that dumbbells remain in proper position
- Feel increased muscle activation from added weight
- Maintain breathing pattern despite increased effort
Step 6: Powerful Weighted Ascent
Rising from the bottom position while holding dumbbells when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly demands greater force production from your legs. Drive powerfully through the front heel while maintaining control of the dumbbells. The additional weight makes this phase more challenging but also more beneficial for strength development when executed properly.
- Drive forcefully through front heel against added resistance
- Keep dumbbell position stable during ascent
- Squeeze glutes harder to overcome additional weight
- Control the rise to maintain dumbbell positioning
Step 7: Safe Weight Return
Completing the movement and returning to starting position when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly with dumbbells requires careful weight management. Control the forward step of the back foot while maintaining dumbbell position. Set up for the next repetition or safely lower the weights if completing the set, always prioritizing safety over speed.
- Control return step despite weight fatigue
- Maintain dumbbell grip throughout completion
- Set weights down safely between sets
- Check form before continuing with next repetition

How to Do Reverse Lunges Correctly at Home?
Performing reverse lunges at home requires minimal space and no equipment while maintaining the same movement quality as gym-based training. Learning how to do reverse lunges correctly at home makes this exercise accessible regardless of location or equipment availability.
- Clear Adequate Space – Ensure 6-8 feet of clear floor space in all directions to allow full range of movement without obstacles
- Choose Proper Flooring – Use non-slip surfaces like yoga mats on hardwood floors or carpet areas for stability and joint protection
- Create Visual Cues – Use mirrors if available to monitor form, or practice near a wall for balance support during learning phase
- Start with Bodyweight – Master movement pattern without any equipment before progressing to household items for added resistance
- Use Household Items – Progress to water jugs, backpacks filled with books, or laundry detergent containers for makeshift weights
- Maintain Form Focus – Without gym mirrors and trainers, pay extra attention to movement quality and body positioning throughout exercise
- Control Environment – Ensure adequate lighting, comfortable temperature, and remove pets or distractions during workout sessions
- Progress Gradually – Increase repetitions, sets, or add pause holds before incorporating external resistance from household items
- Practice Consistency – Home training allows for daily practice of movement patterns, leading to faster skill development and strength gains
- Safety First – Keep first aid supplies accessible and inform others in home about your workout schedule for safety purposes
Check out calories burned in lunges to understand the energy expenditure of your home workouts.
Reverse Lunges Calories Burned
Understanding calorie burn when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly helps with weight management goals and workout planning. The energy expenditure depends on factors including body weight, exercise intensity, duration, and individual metabolism. This metabolic information guides training decisions for fat loss objectives.
Calorie expenditure during how to do reverse lunges correctly sessions varies significantly based on individual factors and exercise parameters, making it a valuable tool for weight management programs.
| Body Weight (kg) | Calories per 10 Minutes | Calories per 20 Minutes | Calories per 100 Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50-60 kg | 60-75 calories | 120-150 calories | 25-30 calories |
| 60-70 kg | 75-90 calories | 150-180 calories | 30-35 calories |
| 70-80 kg | 90-105 calories | 180-210 calories | 35-40 calories |
| 80-90 kg | 105-120 calories | 210-240 calories | 40-45 calories |
| 90+ kg | 120+ calories | 240+ calories | 45+ calories |
Learn about 500 skipping burns how many calories for comparison with other exercises.
Factors Affecting Calorie Burn
Several variables influence energy expenditure when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly, affecting the total calories burned during exercise sessions. Understanding these factors helps optimize workout planning for weight management and fitness goals.
- Body Weight and Composition – Heavier individuals burn more calories per minute, while higher muscle mass increases metabolic rate during exercise
- Exercise Intensity and Speed – Faster movement tempo and explosive power generate higher calorie expenditure than slow, controlled movements
- Range of Motion Depth – Deeper lunges with full range of motion require more energy than partial or shallow movement patterns
- Rest Periods Between Sets – Shorter rest periods maintain elevated heart rate and increase overall caloric expenditure during workout sessions
- Added Resistance Weight – External weights like dumbbells or household items significantly increase energy demands and calorie burning potential
- Workout Duration and Volume – Longer sessions with more sets and repetitions naturally result in higher total calorie expenditure
- Individual Metabolism Rate – Personal metabolic factors including age, gender, and fitness level affect baseline energy expenditure rates
- Environmental Temperature – Hot or cold environments may slightly increase calorie burn as body works to maintain optimal temperature
- Muscle Recruitment Patterns – Better form and full muscle activation patterns increase energy demands compared to inefficient movement
- Pre-Exercise Nutrition Status – Fasted versus fed state can influence substrate utilization and perceived calorie burn during exercise sessions
Maximizing Caloric Expenditure
Optimizing calorie burn while maintaining proper how to do reverse lunges correctly technique involves strategic programming choices including circuit training, plyometric variations, and resistance progression methods.
Practice how to do jumping jacks and learn how many jumping jacks to burn 500 calories.
Reverse Lunge for Glutes
Targeting glute development when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly requires specific technique modifications and programming strategies. The glutes respond particularly well to the hip extension pattern emphasized in reverse lunges, making this exercise excellent for building posterior chain strength and muscle mass.
Optimizing glute activation during how to do reverse lunges correctly involves focusing on specific movement cues and technique refinements that maximize muscle recruitment patterns.
Maximizing Glute Activation Techniques
The reverse lunge naturally emphasizes the glutes more than forward variations due to the hip extension pattern required during the ascent phase. To maximize glute engagement when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly, focus on pushing through the heel of the front foot while driving the hip forward. Maintain a slight forward lean of the torso to increase the hip extension range of motion.
Programming for Glute Development
Programming reverse lunges for glute development requires strategic set and rep schemes that promote muscle growth and strength. Higher rep ranges of 12-20 repetitions with moderate resistance often prove most effective for glute hypertrophy when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly. Consider adding pause reps at the bottom position to increase time under tension and enhance the mind-muscle connection.
Advanced Glute-Focused Variations
Advanced practitioners learning how to do reverse lunges correctly can incorporate specific modifications to further target glute development. Deficit reverse lunges performed on an elevated surface increase the range of motion and glute stretch. Single-leg reverse lunges to high knee drive combinations add dynamic hip flexion that pre-stretches the glutes for enhanced activation during subsequent repetitions.
Explore how to do bicycle crunches to complement your lower body training with core strengthening.

Variation in Reverse Lunges
Mastering different variations when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly prevents training plateaus and targets muscles from various angles. These modifications range from beginner-friendly options to advanced challenges that test strength, balance, and coordination. Variation keeps training interesting while promoting continued adaptation.
Progressive variations of how to do reverse lunges correctly allow for systematic advancement from basic movements to complex, multi-planar challenges that enhance athletic performance and functional capacity.
- Bodyweight Reverse Lunges – Foundation movement focusing on form mastery and movement pattern development
- Dumbbell Reverse Lunges – Added resistance for strength development using dumbbells held at sides or shoulders
- Barbell Reverse Lunges – Heavy loading option with barbell across upper back for maximum strength gains
- Reverse Lunge with Knee Drive – Add knee drive at top for core activation and balance challenge
- Lateral Reverse Lunges – Step back and out at 45-degree angle to target different muscle fibers
- Reverse Lunge to High Knee – Combine with high knee lift for added core and hip flexor activation
- Jumping Reverse Lunges – Plyometric version for power development and cardiovascular conditioning
- Deficit Reverse Lunges – Perform on elevated surface for increased range of motion and glute stretch
- Single-Arm Reverse Lunges – Hold weight in one hand to challenge core stability and anti-rotation strength
- Reverse Lunge with Rotation – Add torso rotation for multi-planar movement and enhanced athletic transfer
Understanding can hiit build muscle and explore calisthenics equipment for home for training variety.
Beginner Variations
Starting variations when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly include assisted options and reduced range of motion movements that build confidence while developing proper movement patterns safely.
Advanced Progressions
Advanced variations of how to do reverse lunges correctly challenge experienced trainees with complex movement patterns, unstable surfaces, and multi-planar demands that enhance athletic performance significantly.
Learn about hack squat vs leg press to understand different approaches to leg training.
Common Mistakes and How to Fix Them
Avoiding common errors when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly ensures optimal results while preventing injury risk. Recognition and correction of these issues before they become ingrained movement patterns accelerates skill development and maximizes exercise benefits.
- Putting Too Much Weight on Back Foot – Keep 80% of weight on front leg throughout movement; focus on front leg doing the work while back leg provides balance only
- Front Knee Drifting Forward – Ensure front knee stays directly above ankle; step back farther if knee moves past toes during descent phase
- Leaning Forward Excessively – Maintain upright torso with shoulders back; engage core muscles to prevent forward lean and protect lower back
- Taking Too Short Steps – Step back 2-3 feet to allow proper 90-degree knee angles; short steps prevent full range of motion and muscle activation
- Rushing the Movement – Control both descent and ascent phases; slow, deliberate movements enhance muscle activation and reduce injury risk significantly
- Allowing Knee to Cave Inward – Keep front knee tracking over middle toe; strengthen hip abductors and focus on proper hip and ankle alignment
- Not Reaching Full Depth – Lower until back knee nearly touches floor; partial range of motion limits muscle development and functional benefits
- Using Back Leg to Push Off – Drive primarily through front heel during ascent; back leg should assist minimally with balance rather than power generation
- Holding Breath During Movement – Maintain steady breathing pattern; exhale during exertion phase and inhale during lowering to optimize performance
- Neglecting Core Engagement – Keep abdominal muscles active throughout exercise; strong core protects spine and improves overall movement quality and stability
Discover how many burpees a day to add cardiovascular training to your routine.
Safety Tips and Precautions
Prioritizing safety when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly prevents injuries and ensures long-term training success. Proper preparation, progressive loading, and attentiveness to body signals create optimal conditions for safe and effective exercise performance. These precautions become especially important as exercise intensity increases.
Following established safety protocols maximizes the benefits of learning how to do reverse lunges correctly while minimizing risks associated with lower body training activities.
- Proper Warm-Up Essential – Complete 5-10 minutes of dynamic movement before attempting reverse lunges
- Start with Bodyweight – Master movement pattern without external resistance before adding weights
- Progress Gradually – Increase difficulty, range of motion, or load by small increments weekly
- Monitor Knee Alignment – Keep front knee tracking over middle toe throughout entire movement
- Maintain Core Engagement – Keep abdominal muscles active to protect spine and improve stability
- Choose Appropriate Surface – Use non-slip flooring with adequate space for full movement range
- Listen to Your Body – Stop immediately if experiencing pain, dizziness, or unusual discomfort
- Allow Recovery Time – Rest 48-72 hours between intense lower body training sessions
- Stay Hydrated – Maintain proper fluid intake before, during, and after exercise sessions
- Seek Professional Guidance – Consider working with qualified trainer when learning proper technique
Understanding calisthenics for triceps helps balance your training with upper body strengthening.
Programming Reverse Lunges in Your Workout
Incorporating reverse lunges into your training program when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly requires strategic planning to optimize results while allowing adequate recovery. Consider your fitness goals, current strength level, and other exercises when determining frequency, volume, and intensity.
| Training Level | Sets | Reps Per Leg | Frequency | Rest Between Sets | Progression Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | 2-3 | 8-12 | 2-3x/week | 60-90 seconds | Master bodyweight form first |
| Intermediate | 3-4 | 10-15 | 3x/week | 45-75 seconds | Add light dumbbells gradually |
| Advanced | 4-5 | 12-20 | 3-4x/week | 30-60 seconds | Heavy weights, explosive variants |
| Strength Focus | 3-5 | 5-8 | 3x/week | 2-3 minutes | Progressive overload with weights |
| Hypertrophy | 3-4 | 12-20 | 3-4x/week | 45-90 seconds | Higher volume, moderate weights |
| Endurance | 2-4 | 15-25 | 4-5x/week | 30-45 seconds | Bodyweight, circuit training |
| Athletic Performance | 3-4 | 8-12 | 3x/week | 60-90 seconds | Plyometric and loaded variations |
| Rehabilitation | 2-3 | 10-15 | 2-3x/week | 90-120 seconds | Focus on form, light resistance |
Effective programming of how to do reverse lunges correctly balances training stress with recovery to promote adaptation and prevent plateaus or injuries throughout your fitness journey.
Learn about calisthenics vs weightlifting to understand different training approaches.
Conclusion
Mastering how to do reverse lunges correctly provides an excellent foundation for lower body strength, balance, and functional movement. This exercise delivers unmatched benefits including improved glute activation, reduced knee stress, and enhanced stability compared to other lunge variations. Focus on proper form, gradual progression, and consistent practice to maximize results while minimizing injury risk.
Master how to lift heavier weights, understand what is foam rolling, try chest and tricep workout with dumbbells, explore bodybuilding exercises at home, and practice calisthenics chest exercises.
Want to master the calisthenics handstand and take your skills to the next level? Whether you’re a beginner or pushing advanced skills, ISC – Indian School of Calisthenics offers expert guidance to help you master bodyweight training. Visit us at SRPF Ground, NH8, Goregaon (E), Mumbai – 400065. For class schedules, personalized coaching, or more details, call +91 77159 53218. Train smart, move better, and unlock your back strength with ISC.
How to Do Reverse Lunges Correctly? – FAQs
What is the proper starting position when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Stand with feet hip-width apart, shoulders back, core engaged, and weight evenly distributed before stepping backward.
How far should I step back when performing how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Step back approximately 2-3 feet or far enough to achieve 90-degree angles in both knees at the bottom position.
Which muscles are primarily targeted when you know how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Reverse lunges primarily target glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, with secondary activation of core muscles and calves for stability.
Are reverse lunges better than forward lunges for beginners learning how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Yes, reverse lunges are generally safer for beginners because they provide better knee positioning and stability control.
How many repetitions should I do when first learning how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Start with 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions per leg, focusing on perfect form rather than high volume.
Can I add weights when learning how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Yes, but master bodyweight technique first, then gradually add dumbbells or other resistance for progressive overload.
What’s the most common mistake when trying to learn how to do reverse lunges correctly?
The most common mistake is putting too much weight on the back foot instead of keeping 80% weight on the front leg.
How often should I practice learning how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Practice reverse lunges 2-3 times per week with 48-72 hours rest between sessions for optimal recovery and adaptation.
Can people with knee problems safely learn how to do reverse lunges correctly?
Yes, reverse lunges are often recommended for knee issues because they reduce joint stress compared to forward lunges.
How do I progress after mastering how to do reverse lunges correctly with bodyweight?
Progress by adding dumbbells, increasing repetitions, trying single-arm variations, or incorporating plyometric elements for advanced challenge.